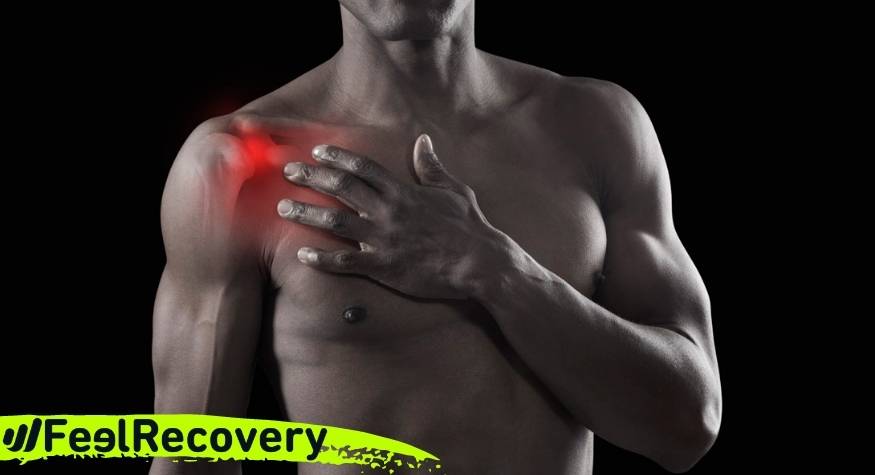
- What are pectoralis muscle strains?
- What are the causes of muscular strains in the chest?
- Best products for chest muscle cramps
- Main symptoms associated with pectoral muscle strains
- How to relieve the pain and improve the symptoms of chest muscle contractures?
- What are the most effective methods of prevention for pulled muscles strains in the chest?
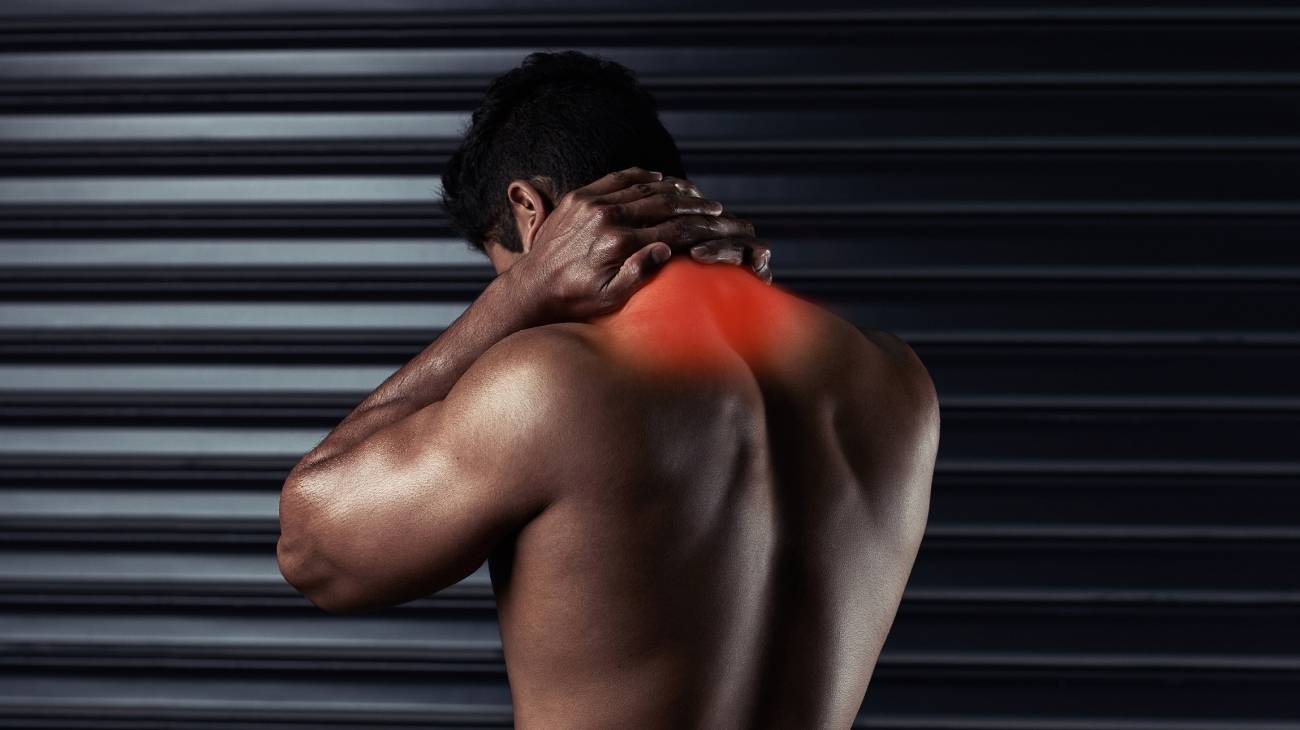
Fatigue caused by overexertion as well as lack of movement in the pectoral muscles can develop a strains in the chest. This action generates involuntary tension in the muscle structure and the patient will feel pain and inflammation.
If you want to know more about what a pectoral pull is, we invite you to continue reading this article. We will explain in an easy and detailed way what are the causes that originate this ailment in the pectoral muscles and its main symptoms. In addition, you can read about the treatments that help to improve the pain. Let's get started.
What are pectoralis muscle strains?
Pectoralis muscle strains are caused by the accumulation of metabolites in the soft tissue fibres. These wastes cannot be discharged into the bloodstream due to their inability to reach this area of the body in the normal way.
Thus, the muscles begin to maintain an involuntary stiffness causing inflammation and pain in the patient's chest. The reasons for the appearance of this injury are varied, although it is generally due to excessive strength, a sedentary lifestyle or poor diet.
What are the causes of muscular strains in the chest?
We will mention below all the situations that increase the chances of the appearance of a muscular contracture in the chest
- Overexertion: Ex cessive or prolonged force on the muscles leads to metabolites in the soft tissue. This leads to muscle pulls in the chest.
- Muscle fatigue: The lack of constant movement in the pectoral muscles leads to a different tension in the pectoral muscles than normal. This means that when the chest muscles have to be strained for any activity, fatigue is felt, which can lead to muscle stiffness in this area.
- Lack of magnesium and potassium: These nutrients regulate the function of the muscles, causing the sugar levels to be correct. If a person has low levels of these elements, the likelihood of chest strain increases.
- Trauma: Both blows and injuries caused by wounds can cause muscles to tighten involuntarily.
- Bad posture: The appearance of strains in the chest can be caused by incorrectly adopted positions to perform force or a specific task. For this reason, it is advisable to take into account the weight of the object to be lifted, the time the activity will take and the physical comfort to perform the task.
- Lack of muscle warm-up before performing a sporting exercise: It is common to find injuries in the pectorals due to lack of activity with gradual growth before carrying out demanding movements. This is also related to the lack of pre- and post-stretching that athletes or workers who make demands on this part of the body must perform.
- Repetitive movements: This kind of action also puts the body at an extreme limit in terms of the tension on the muscular structure in the chest area. For this reason, it is advisable to rest in between tasks.
- Stress: People with a high level of stress are more likely to keep the muscles in this area tense, which will lead to the appearance of a muscle contracture.
- Age: While it is true that muscle pulls can occur in anyone, it is common to find patients with this type of ailment who are over 60 years of age. This is due to loss of muscle flexibility.
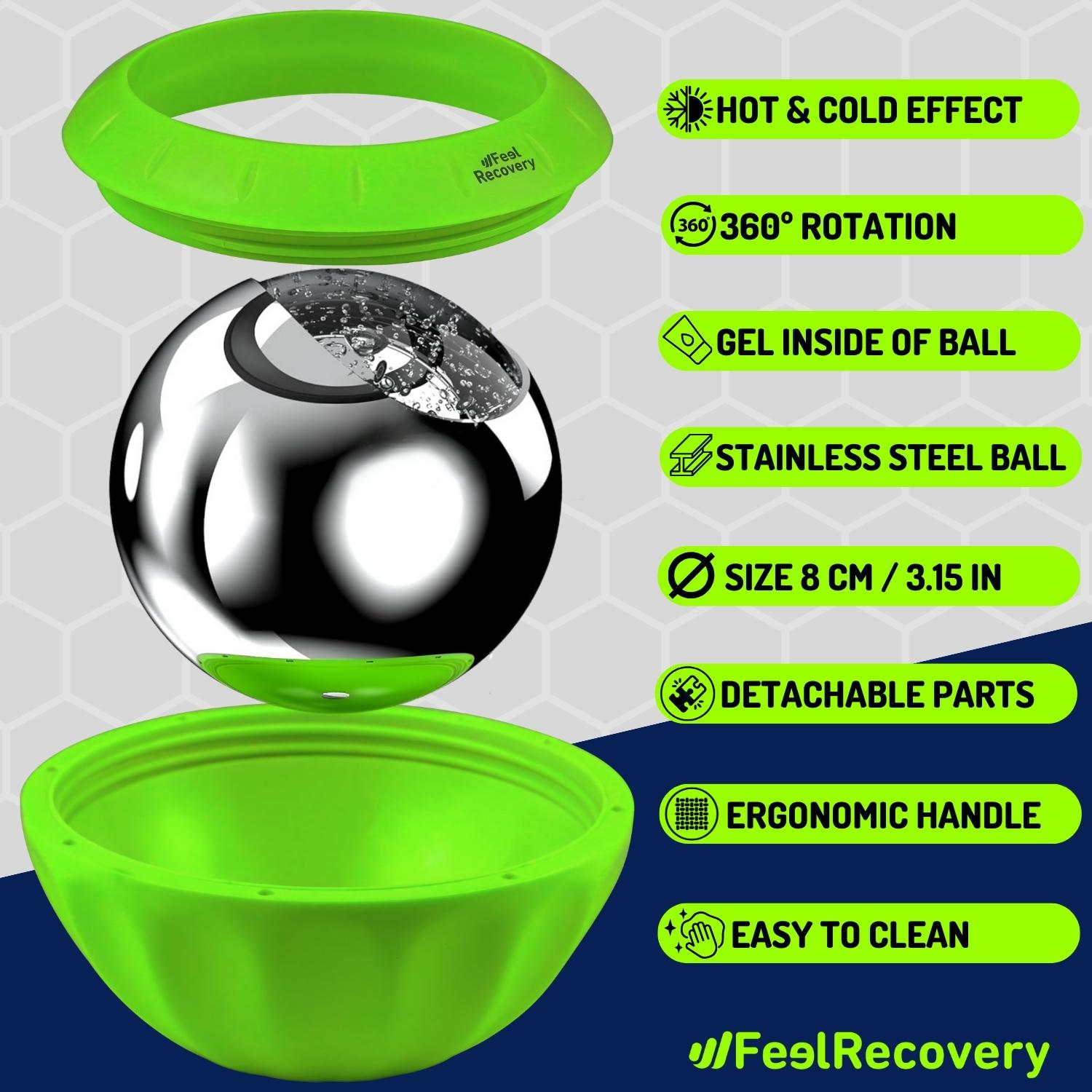
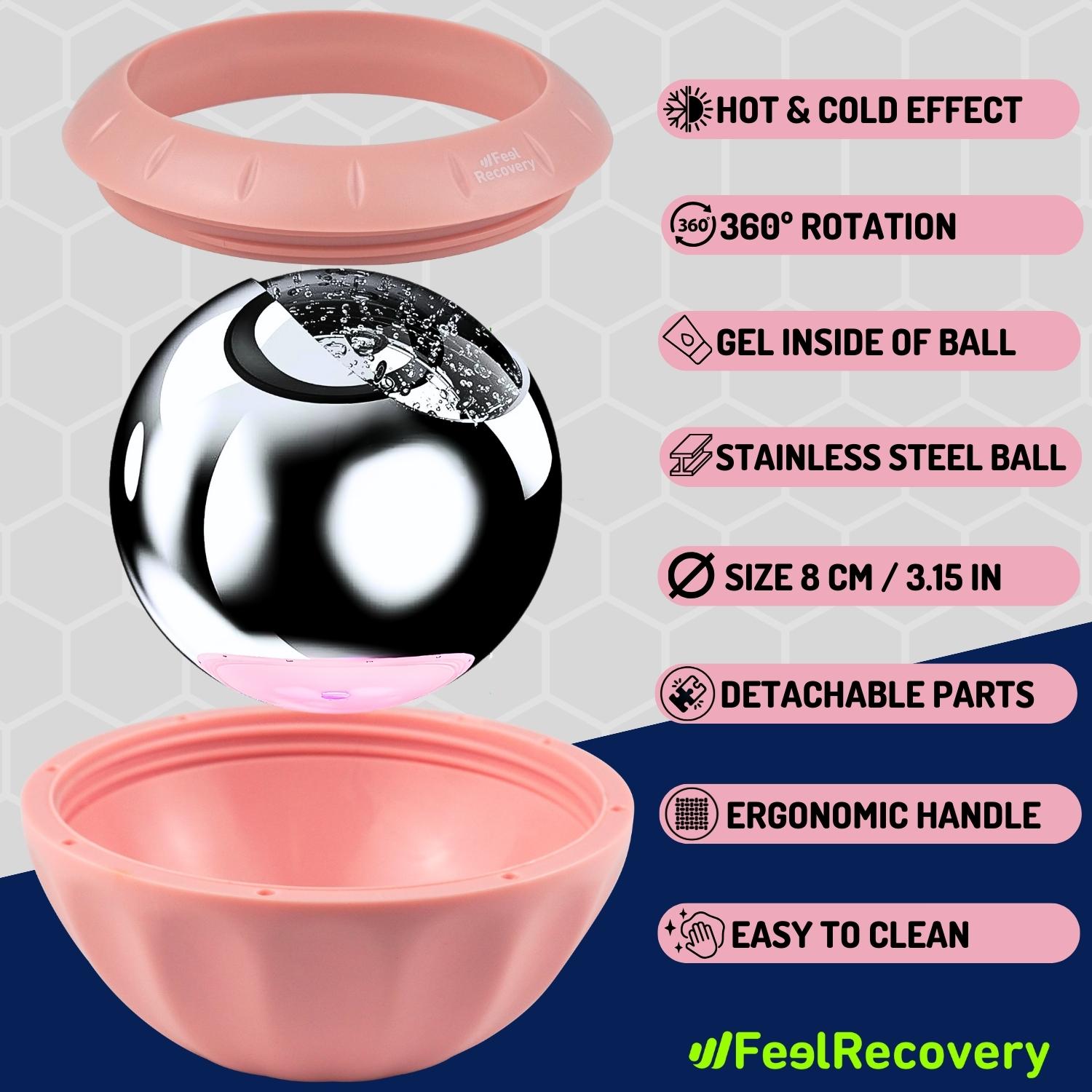
Best products for chest muscle cramps
Bestseller
-
Acupressure Mat and Pillow (Black/Gray)
$49.95 -
Acupressure Mat and Pillow (Green/Navy)
$49.95 -
Acupressure Mat and Pillow (Pink/Bordeaux)
$49.95 -
Acupressure Pillow (Black/Gray)
$29.46 -
Acupressure Pillow (Green/Navy)
$29.46 -
Acupressure Pillow (Pink/Bordeaux)
$29.46 -
High Density Foam Roller for Muscle (Black/Gray)
$29.95 -
High Density Foam Roller for Muscle (Green/Navy)
$29.95 -
High Density Foam Roller for Muscle (Pink/Bordeaux)
$29.95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Black)
$39.95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Green)
$39.95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Pink)
$39.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Hearts)
$24.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Oxford)
$24.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Sport)
$24.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Hearts)
$19.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Oxford)
$19.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Sport)
$19.95 -
Pack 2 In 1 Foam Roller High + Soft Density (Black/Gray)
$29.95 -
Pack 2 In 1 Foam Roller High + Soft Density (Green/Navy)
$29.95 -
Pack 2 In 1 Foam Roller High + Soft Density (Pink/Bordeaux)
$29.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Black)
$24.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Green)
$24.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Pink)
$24.95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Black)
$29.95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Green)
$29.95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Pink)
$29.95 -
Trigger Point Massage Stick (Black)
$14.95 -
Trigger Point Massage Stick (Green)
$14.95 -
Trigger Point Massage Stick (Pink)
$14.95
Main symptoms associated with pectoral muscle strains
It is possible to know in advance of a doctor's visit if you are suffering from a pectoral muscle strain by looking at these symptoms
- Inflammation: This symptom is frequent in chest strain lessons. This is due to the involuntary tension that the trapezius has, causing the blood flow to be unable to eliminate the metabolic molecules that are generated in this tissue.
- Constant pain: This sign may be caused by pressure on the nerves located in this area of the body. In addition, muscle stiffness causes the patient to be unable to move the arm, waist and even the neck,
- Appearance of nodules: Lumps are common in this type of injury, as they are muscles that are abnormally stiff. This may also be caused by inflammation suffered by other anatomical areas such as bursae and tendons.
- Spasms: These types of involuntary actions are common in pectoral muscle injuries.
- Loss of strength: The muscular pulls produced in the chest cause fatigue, thus generating a decrease in energy on the part of the patient.
- Bruising: In some cases it is possible to find blood trapped under the skin due to lack of proper blood flow.
How to relieve the pain and improve the symptoms of chest muscle contractures?
It is possible to improve the symptoms and relieve the pain of pectoral muscle strains through the application of different treatments, which should be practised and directed by the doctor.
See below all the therapies currently in use:
Alternative and complementary therapies
Complementary therapies are those procedures that are used to accompany different treatments that help to reduce the symptomatology of chest muscle distension.
Among the most important are:
- Heat and cold therapy: It has been shown that cold is not advisable to reduce the symptoms of chest muscle strain. But by means of controlled therapy in terms of application, the analgesic benefits of this type of temperature can be obtained. As far as heat is concerned, the correct temperature is assigned by means of compresses, electric blankets or water bags in order to generate anti-inflammatory benefits. This therapy must be carried out by a professional and the sessions should not exceed 15 to 20 minutes, always starting with heat, continuing with cold and finishing with warm or hot elements.
- Compression therapy: In muscular contracture of the pectoral muscles it is possible to apply this compression therapy, which includes elastic bandages and other types of compressive clothing that allow the chest to be kept as relaxed as possible. This should be accompanied by rest to improve the immobilisation of the area. It should not be forgotten that the pressure exerted on this area of the body must be correct so as not to interfere with the respiratory or gastric system. In addition, with a balanced tension it is possible to stimulate the body's blood vessels.
- Massage therapy: In this type of treatment, the aim is to reduce inflammation and pain by means of pressure techniques, which can be applied with the masseur's hands or with other elements. Once the bloodstream is activated, the blood begins to circulate better through the affected area, thus causing the creation of endorphins that act as painkillers. This also helps to reduce stress by lowering the overall tension in the muscle structure.
- Acupressure therapy: This oriental medicine is based on manual finger and palm massages performed at strategic points on the body, causing the patient's stress to decrease and improving the general feeling of well-being. For this reason, acupressure helps to release endorphins to produce natural painkillers.
- Thermotherapy: Among the most important benefits of thermotherapy is the stimulation of capillary vessels to promote proper blood circulation. This treatment can be applied in various ways, the most common being the use of electric blankets or hot water bottles. In more advanced cases, ultrasound therapy is used to generate internal heat in the pectorals.
- Natural remedies using plants: It is possible to reduce the symptoms of chest muscle strain by using medicinal plants. This is done by means of an infusion or tea, which must be ingested by the patient to obtain the analgesic and anti-inflammatory benefits, although it is also possible to find herbs with natural muscle relaxants. Because of this, willow, rosemary, citrus fruits and linden are frequently used in this therapy.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: This therapy is directed by the acting doctor and involves explaining to the patient the different habits he/she should include in his/her life in order to improve the symptoms of strain and avoid future injuries. In this way, the patient is taught, among other things, to sleep properly, to eat different foods necessary to strengthen the muscular system and to exercise regularly.
Nutritional supplements
It is possible to reduce the symptomatology of muscular contractures suffered in the pectoral muscles by incorporating nutrients into the patient's diet. This allows the muscular system to benefit, resulting in greater flexibility. Among the most commonly used supplements are vitamin D and E, B group, magnesium, calcium and potassium. The most common forms are pills, liquids and powders.
Physiotherapy treatments
The aim of this type of therapy is the functional readaptation of the pectoral muscles. This will be done by means of different techniques, which will be in charge of the physiotherapist who can include repetitive exercises under water, activities with elements that locally stimulate the musculature, ultrasound (to speed up the activation of the blood fluid in the tissues), laser therapy and massages by small blows or slides of the hands or therapeutic artefacts.
Medications
The drugs used for the treatment of shoulder and trapezius muscle strains are based on anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen. Although it is also possible to apply muscle relaxants that will help to decompress the tension in this area of the body. In some cases, opioid analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Keep in mind that meditation must be prescribed by a doctor, and taking medication on your own can have harmful consequences for the intestinal and hepatic systems. In addition, it can aggravate the symptoms of muscular distension. For this reason it is never advisable to self-medicate
What are the most effective methods of prevention for pulled muscles strains in the chest?
You will be able to prevent the onset of pulled chest muscles if you take into account a few methods that will help you to avoid this strain.
Read on for a complete list of each of these effective methods
- Use heat: Don't forget that thermotherapy helps the dilator vessels to work better, causing a greater flow of blood to the chest muscles. This will prevent the tradition of pulling in this part of the body because the tissue will be prepared for the extra demand.
- Warm up the muscle structure before exercising: It is important that you gradually build up your pecs. This means that you will have to stretch them before starting a task or a sporting activity. In this way, stretching will prevent the accumulation of metabolites in the soft tissue.
- Avoid a sedentary lifestyle: Recurrent exercise helps to keep the chest muscles active, which improves the blood flow in this area and allows acids and gases to be exchanged with the blood more efficiently.
- Correct your posture: You must not forget that one of the main causes of the appearance of distinctions in the chest is exaggerated and poorly performed strength in this area of the body. For this reason, when you have to lift heavy things or perform any activity in which the pectoral muscles are affected, it is recommended that you perform the task with the correct posture and position of the muscles.
- Stretch after activities: Stretching the muscles will help you to keep the correct tension of the pectorals active. To do this, you should consult a doctor about which exercises are suitable for stretching the chest muscles correctly.
- Maintain a balanced diet: The inclusion of potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium and vitamins will help you to balance the nutrients your body needs. This will ensure that the muscles always have the correct tension and strength to withstand excessive work or measuring forces. This includes good hydration.
- Avoid high-risk activities: Both sports and jobs in which you can receive blows to the chest can cause chronic contractures. For this reason it is advisable to avoid this type of activity or to protect this area with suitable compression clothing.
- Choose relaxation techniques: Both massages and meditation help to maintain mental balance, causing stress to decrease and muscles to maintain proper toning. This will prevent the appearance of distinctions.
- Practice activities with gradual progress: You should keep in mind that when you start any sport or simply realised that walking or cycling half an hour a day is a good preventive idea, you should do it with progressive efforts. This means that on the first day you should not exercise your body to the maximum level of demand.
- Don't smoke or drink alcohol: These substances cause the blood to be unable to eliminate the remains of metabolic molecules in the fibres of the pectoral muscles, which will increase the likelihood of contracting a pulled chest muscle.
References
- Ayloo, A., Cvengros, T., & Marella, S. (2013). Evaluation and treatment of musculoskeletal chest pain. Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice, 40(4), 863-887. https://www.primarycare.theclinics.com/article/S0095-4543(13)00088-2/fulltext
- Sik, E. C., Batt, M. E., & Heslop, L. M. (2009). Atypical chest pain in athletes. Current sports medicine reports, 8(2), 52-58. https://journals.lww.com/acsm-csmr/Fulltext/2009/03000/Atypical_Chest_Pain_in_Athletes.7.aspx
- Hopper, M. A., Tirman, P., & Robinson, P. (2010, June). Muscle injury of the chest wall and upper extremity. In Seminars in musculoskeletal radiology (Vol. 14, No. 02, pp. 122-130). © Thieme Medical Publishers. https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-0030-1253156
- Petilon, J., Carr, D. R., Sekiya, J. K., & Unger, D. V. (2005). Pectoralis major muscle injuries: evaluation and management. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 13(1), 59-68. https://journals.lww.com/jaaos/Abstract/2005/01000/Pectoralis_Major_Muscle_Injuries__Evaluation_and.8.aspx
- Gregory, P. L., Biswas, A. C., & Batt, M. E. (2002). Musculoskeletal problems of the chest wall in athletes. Sports Medicine, 32, 235-250. https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165/00007256-200232040-00003
- Glick, J. M. (1980). Muscle strains: prevention and treatment. The Physician and sportsmedicine, 8(11), 73-77. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00913847.1980.11710969
- Garrett Jr, W. E. (1996). Muscle strain injuries. The American journal of sports medicine, 24(6_suppl), S2-S8. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/036354659602406S02
- Orchard, J., Best, T. M., & Verrall, G. M. (2005). Return to play following muscle strains. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, 15(6), 436-441. https://journals.lww.com/cjsportsmed/Abstract/2005/11000/Return_to_Play_Following_Muscle_Strains.8.aspx
- Garrett Jr, W. E. (1990). Muscle strain injuries: clinical and basic aspects. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 22(4), 436-443. https://europepmc.org/article/med/2205779
- Järvinen, T. A., Kääriäinen, M., Järvinen, M., & Kalimo, H. (2000). Muscle strain injuries. Current opinion in rheumatology, 12(2), 155-161. https://journals.lww.com/co-rheumatology/Abstract/2000/03000/Muscle_strain_injuries.10.aspx