Preventing sports injuries is crucial for athletes of all levels, from amateurs to professionals. Sports injuries can not only impact an athlete's immediate performance but can also have long-lasting effects on their health and future athletic endeavors. The importance of injury prevention in sports cannot be overstated. Athletes need to be aware of the most common risk factors for sports injuries, such as overuse, improper technique, and inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines.
It is also essential to incorporate effective strengthening and conditioning exercises, as well as flexibility training, into their routines. Proper technique and form during sports activities are equally critical in preventing injuries. By taking proactive measures to prevent injuries, athletes can ensure they stay in top physical condition and reduce their risk of injuries, which can ultimately help them achieve their athletic goals.
Best sports injury prevention products
bestseller
-
2 Ankle Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
$24.95 -
2 Ankle Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
$24.95 -
2 Ankle Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
$24.95 -
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
$24.95 -
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
$24.95 -
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
$24.95 -
2 Elbow Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
$24.95 -
2 Elbow Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
$24.95 -
2 Elbow Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
$24.95 -
2 Knee Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
$24.95 -
2 Knee Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
$24.95 -
2 Knee Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
$24.95 -
2 Thigh Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
$24.95 -
2 Thigh Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
$24.95 -
2 Thigh Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
$24.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Hearts)
$29.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Oxford)
$29.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Sport)
$29.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Hearts)
$24.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Oxford)
$24.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Sport)
$24.95
-
Back Support Belt (Black)
$49.95 -
Back Support Belt (Green)
$49.95 -
Back Support Belt (Pink)
$49.95 -
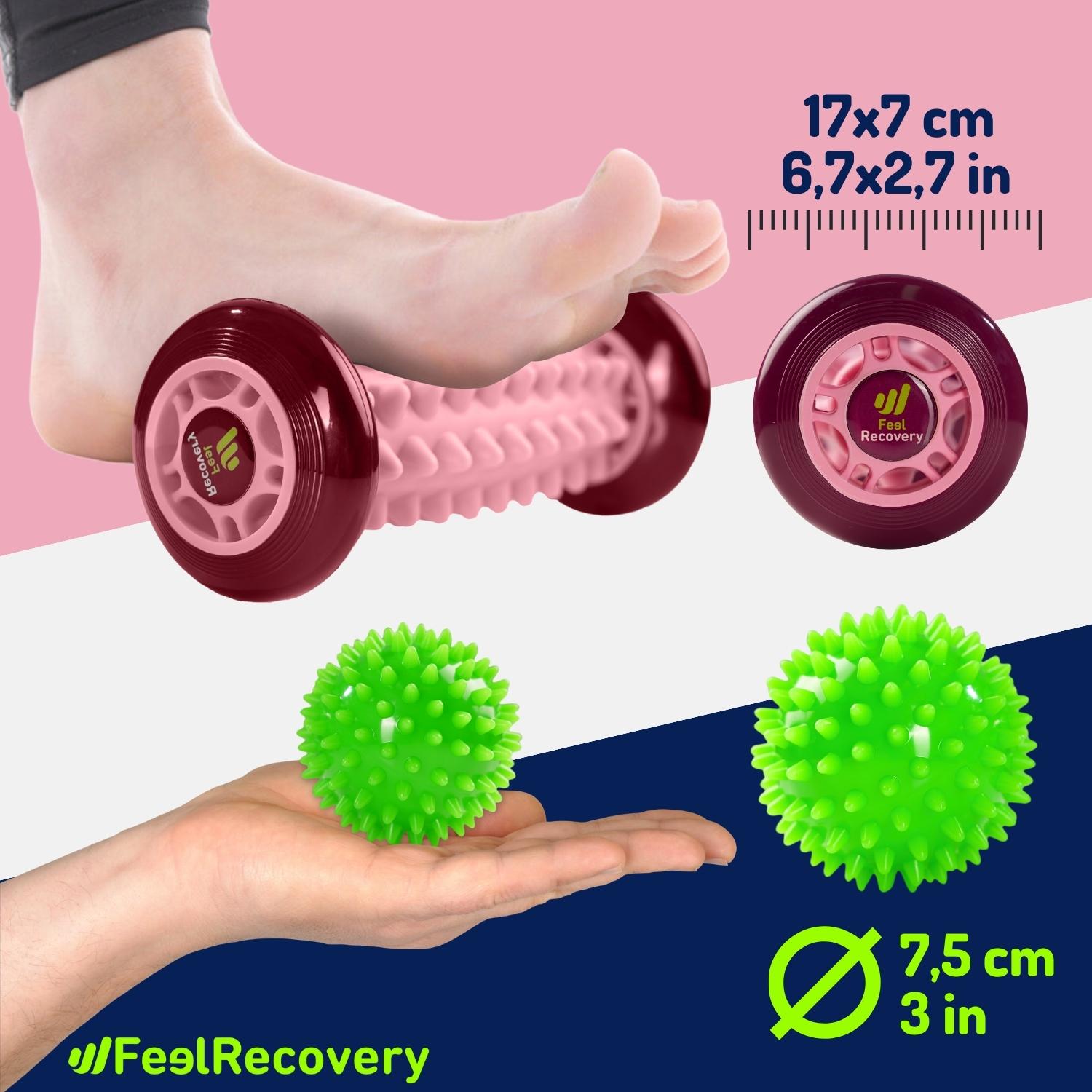
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Black)
$24.95 -
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Green)
$24.95 -
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Pink)
$24.95 -
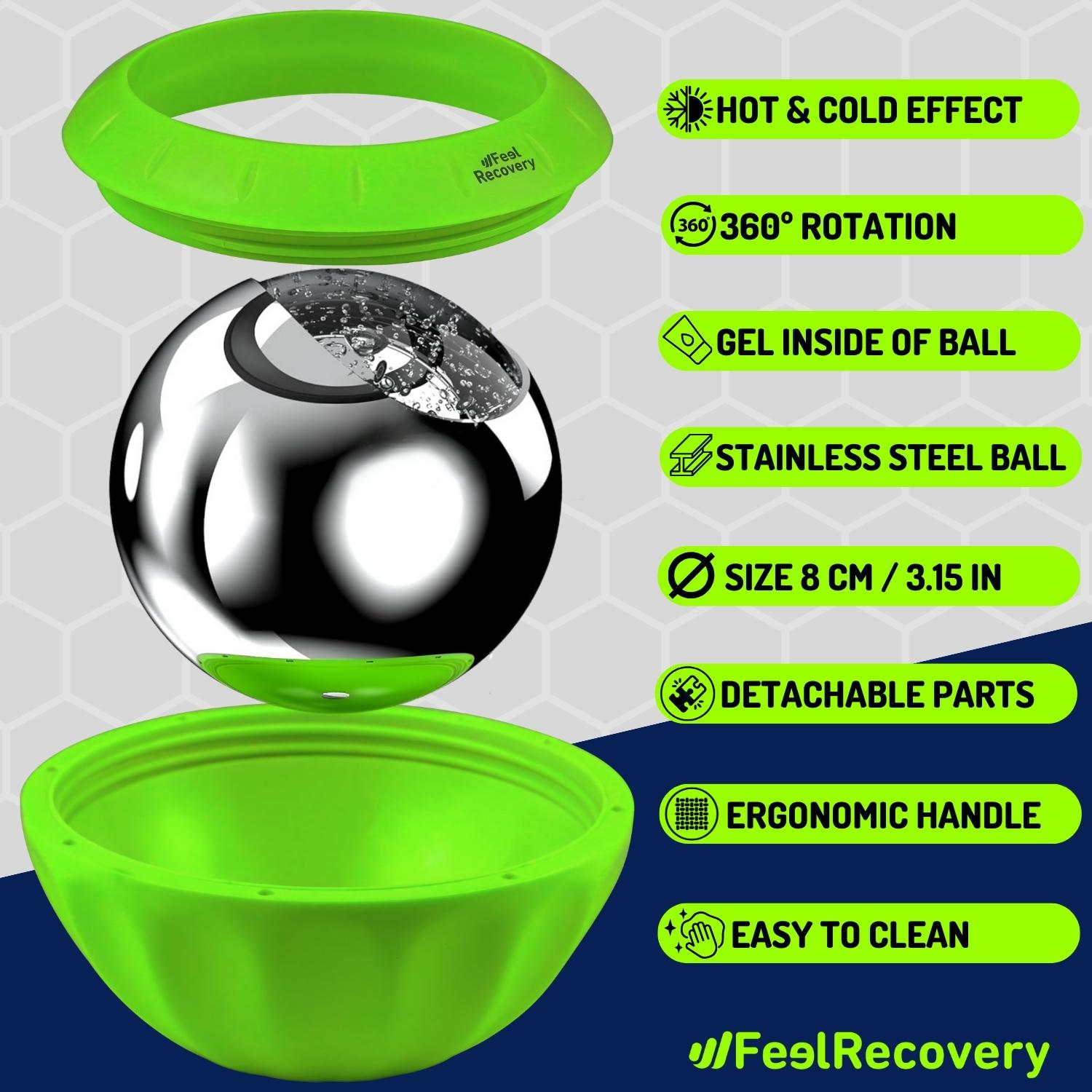
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Black)
$39.95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Green)
$39.95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Pink)
$39.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Black)
$29.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Green)
$29.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Pink)
$29.95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Black)
$39.95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Green)
$39.95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Pink)
$39.95
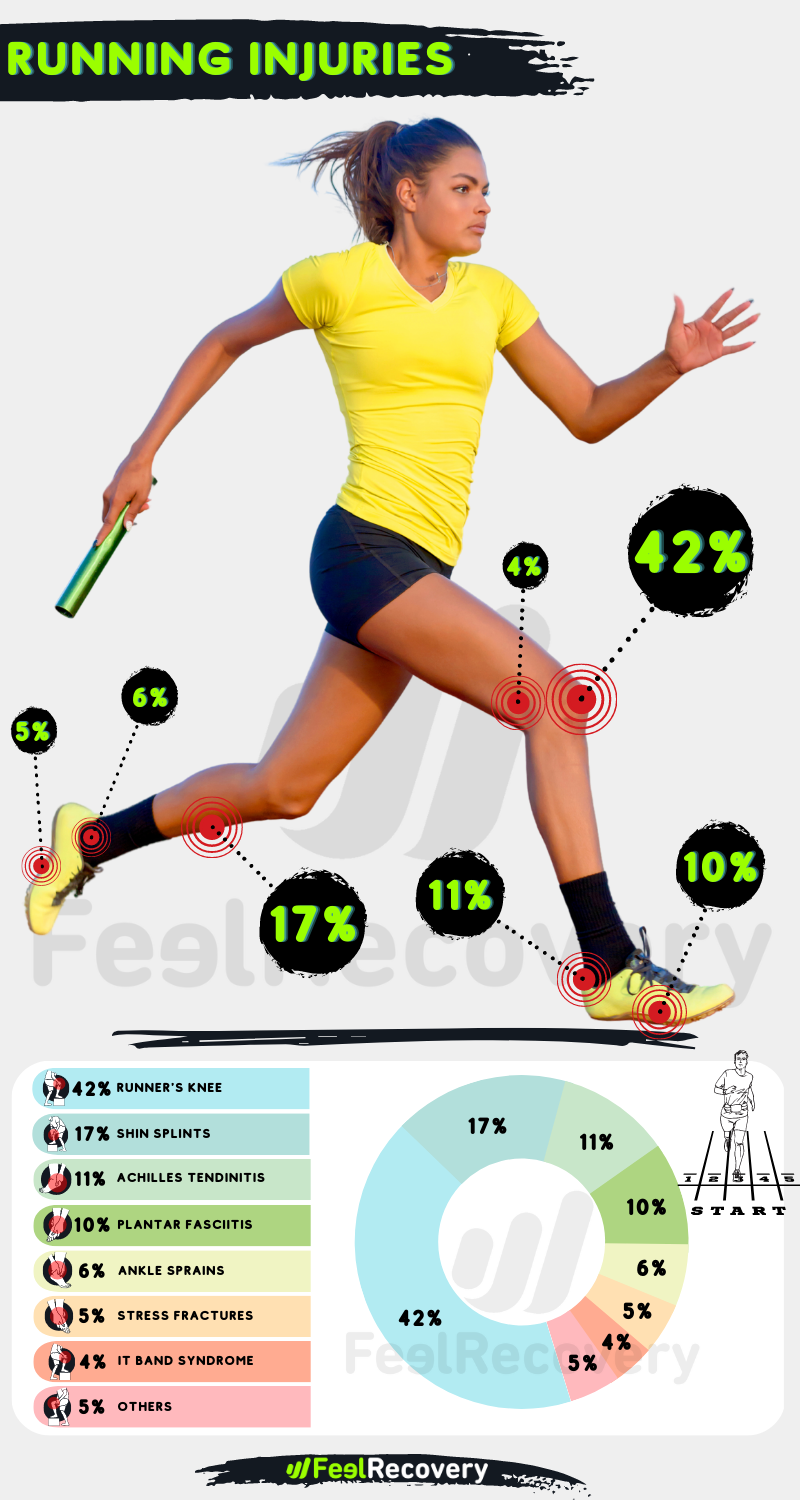
What are the most common sports injuries?
There are many different types of injuries that people can experience, but here are 15 of the most common:
- Sprains and Strains: These injuries involve damage to muscles, tendons, or ligaments, typically caused by sudden twisting or stretching.
- Fractures: A fracture occurs when a bone is broken, usually caused by a sudden impact or trauma.
- Contusions: Also known as bruises, contusions occur when small blood vessels under the skin are damaged, usually due to a blunt force impact.
- Cuts and Lacerations: These injuries involve a break in the skin, often caused by sharp objects.
- Burns: Burns can be caused by heat, chemicals, or electricity, and can range in severity from minor to life-threatening.
- Concussions: A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury caused by a blow to the head or body, resulting in temporary loss of brain function.
- Whiplash: Whiplash is a neck injury caused by sudden jerking of the head, often from a car accident.
- Dislocations: Dislocations occur when a joint is forced out of its normal position, usually due to sudden impact or twisting.
- Tendinitis: Tendinitis is an inflammation of a tendon, usually caused by repetitive motion or overuse.
- Bursitis: Bursitis is an inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints, often caused by repetitive motion or pressure.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition caused by compression of the median nerve in the wrist, often due to repetitive motion.
- Tennis Elbow: Tennis elbow is a type of tendinitis caused by overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons.
- Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot, often caused by overuse.
- Stress Fractures: Stress fractures are small cracks in the bone, often caused by repetitive impact or overuse.
- Strains: Strains are injuries to muscles or tendons, usually caused by overuse, fatigue, or improper use.
The impact of these injuries on individuals and society as a whole can be significant. In addition to physical pain and discomfort, injuries can result in lost productivity, missed work or school, and financial strain due to medical expenses and lost income.
Some injuries, such as traumatic brain injuries or spinal cord injuries, can have long-term or permanent effects on an individual's health and quality of life.
Furthermore, the societal impact of injuries can be substantial, including increased healthcare costs, decreased productivity, and reduced quality of life for affected individuals and their families. By taking steps to prevent injuries, we can reduce the personal and societal impact of these common injuries.
Most important risk factors in sports injuries
The 10 most important risk factors for sports injuries:
- Poor conditioning: Inadequate physical conditioning increases the risk of sports injuries. Athletes who do not engage in regular physical activity are more prone to muscle strains, ligament sprains, and other types of injuries.
- Overuse: Overuse injuries occur due to repetitive motions, which place excessive stress on the muscles, joints, and bones. Overuse injuries commonly affect athletes who participate in sports with repetitive movements such as running, swimming, or tennis.
- Lack of proper technique: Improper technique or form during exercise or sports activities can lead to injuries. Athletes who do not learn proper techniques or movements are more likely to suffer from acute injuries.
- Muscle imbalances: Muscle imbalances occur when one muscle group is stronger than its opposing muscle group. These imbalances can lead to joint instability, poor posture, and injuries.
- Insufficient warm-up: Failure to properly warm-up before exercise or sports activities can lead to muscle strains, ligament sprains, and other injuries.
- Inadequate rest and recovery: Inadequate rest and recovery time between training sessions or games can increase the risk of injuries. Athletes need sufficient time to recover and allow their muscles and joints to heal and repair.
- Lack of flexibility: Insufficient flexibility in muscles and joints can lead to injuries. Athletes with poor flexibility are more likely to suffer from muscle strains, joint sprains, and other injuries.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors such as playing surface, weather conditions, and equipment can contribute to sports injuries. Uneven or unstable surfaces can increase the risk of falls, while slippery surfaces can increase the risk of strains and sprains.
- Overtraining: Overtraining occurs when athletes train too frequently, too intensely, or for too long without adequate recovery time. Overtraining can lead to injuries and other health problems.
- Psychological factors: Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression can contribute to sports injuries. These factors can lead to poor decision-making, lack of focus, and decreased performance, which can increase the risk of injuries.
Science-based techniques and methods for sports injury prevention
Here are some of the most effective ones:
- Proper warm-up and cool-down routines: A proper warm-up and cool-down routine can help to increase blood flow to the muscles and prepare the body for the demands of physical activity.
- Correct technique and form: Ensuring that athletes are using proper form and technique during exercises and movements can reduce the risk of injury.
- Gradual progression: Gradually increasing the intensity, frequency, and duration of physical activity can help to prevent overuse injuries.
- Cross-training: Cross-training involves incorporating a variety of different activities and exercises into an athlete's training regimen, which can help to prevent overuse injuries and improve overall fitness.
- Rest and recovery: Rest and recovery are essential for preventing injuries and allowing the body to heal after physical activity.
- Proper nutrition and hydration: Adequate nutrition and hydration can help to support the body during physical activity and reduce the risk of injury.
- Adequate sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for recovery and injury prevention.
- Proper equipment and gear: Ensuring that athletes have proper equipment and gear for their sport can help to reduce the risk of injury.
- Injury prevention programs: Programs designed specifically for injury prevention, such as neuromuscular training and plyometrics, have been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of injury.
- Regular physical exams: Regular physical exams can help to identify any underlying conditions or risk factors that may increase the risk of injury and allow for proper preventative measures to be taken.
Best sports injury prevention and strengthening exercises
Here are the top 10 best injury prevention and strengthening exercises:
- Squats: Squats are a great compound exercise that works multiple muscle groups, including the quads, glutes, and hamstrings. Strong lower body muscles can help prevent knee and ankle injuries.
- Lunges: Similar to squats, lunges target the lower body muscles and improve stability in the hips and knees.
- Deadlifts: Deadlifts are an excellent exercise for strengthening the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back muscles. This can help prevent back and hamstring injuries.
- Planks: Planks target the core muscles, including the abs, obliques, and lower back. A strong core can help prevent back injuries and improve overall stability.
- Push-ups: Push-ups strengthen the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Strong upper body muscles can help prevent shoulder and elbow injuries.
- Pull-ups: Pull-ups work the back, biceps, and forearms. A strong upper back can help improve posture and prevent shoulder injuries.
- Glute bridges: Glute bridges target the glutes and lower back muscles, which can help prevent back and hip injuries.
- Single-leg balance exercises: Single-leg balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or balancing on a wobble board, can help improve balance and prevent ankle injuries.
- Jumping exercises: Jumping exercises, such as box jumps or jump squats, can help improve power and explosiveness in the legs, which can prevent knee and ankle injuries.
- Agility drills: Agility drills, such as ladder drills or cone drills, can help improve coordination, balance, and reaction time, which can prevent a variety of sports injuries.
It's important to note that these exercises should be performed with proper form and under the guidance of a qualified fitness professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. Additionally, incorporating a variety of exercises and targeting all muscle groups can help prevent overuse injuries and promote overall fitness.
It's important to note that these exercises should be performed with proper form and technique to reduce the risk of injury. A qualified fitness professional or physical therapist can help design an individualized exercise plan based on an individual's specific needs and goals.
F.A.Q: Frequently asked questions
References
- Timpka, T., Ekstrand, J., & Svanström, L. (2006). From sports injury prevention to safety promotion in sports. Sports Medicine, 36, 733-745. https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165/00007256-200636090-00002
- Finch, C. (2006). A new framework for research leading to sports injury prevention. Journal of science and medicine in sport, 9(1-2), 3-9. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1440244006000235
- Hübscher, M., Zech, A., Pfeifer, K., Hänsel, F., Vogt, L., & Banzer, W. (2010). Neuromuscular training for sports injury prevention: a systematic review. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 42(3), 413-421. https://bit.ly/3MBqgQ7
- Bahr, R., & Engebretsen, L. (Eds.). (2011). Handbook of sports medicine and science: sports injury prevention (Vol. 17). John Wiley & Sons. https://books.google.es/books?hl=en&lr=&id=YqyDrQ1nLbUC
- Lin, C. Y., Casey, E., Herman, D. C., Katz, N., & Tenforde, A. S. (2018). Sex differences in common sports injuries. PM&R, 10(10), 1073-1082. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1934148218301278
- Skelton, D. A., & Beyer, N. (2003). Exercise and injury prevention in older people. Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports, 13(1), 77-85. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1034/j.1600-0838.2003.00300.x
- Huxel Bliven, K. C., & Anderson, B. E. (2013). Core stability training for injury prevention. Sports health, 5(6), 514-522. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1941738113481200
- Born, D. P., Sperlich, B., & Holmberg, H. C. (2013). Bringing light into the dark: effects of compression clothing on performance and recovery. International journal of sports physiology and performance, 8(1), 4-18. https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/ijspp/8/1/article-p4.xml
- Weerapong, P., Hume, P. A., & Kolt, G. S. (2004). Stretching: mechanisms and benefits for sport performance and injury prevention. Physical Therapy Reviews, 9(4), 189-206. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1179/108331904225007078
- Safran, M. R., Garrett JR, W. E., Seaber, A. V., Glisson, R. R., & Ribbeck, B. M. (1988). The role of warmup in muscular injury prevention. The American journal of sports medicine, 16(2), 123-129. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/036354658801600206