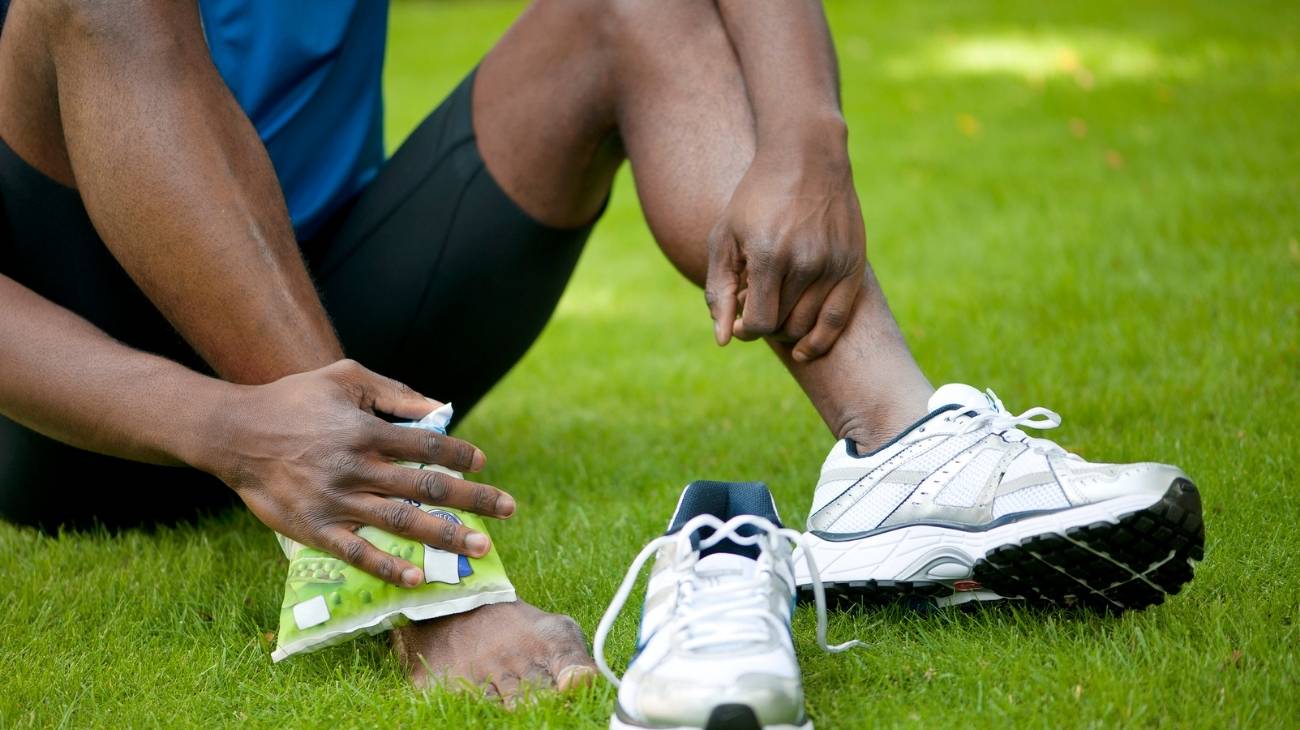
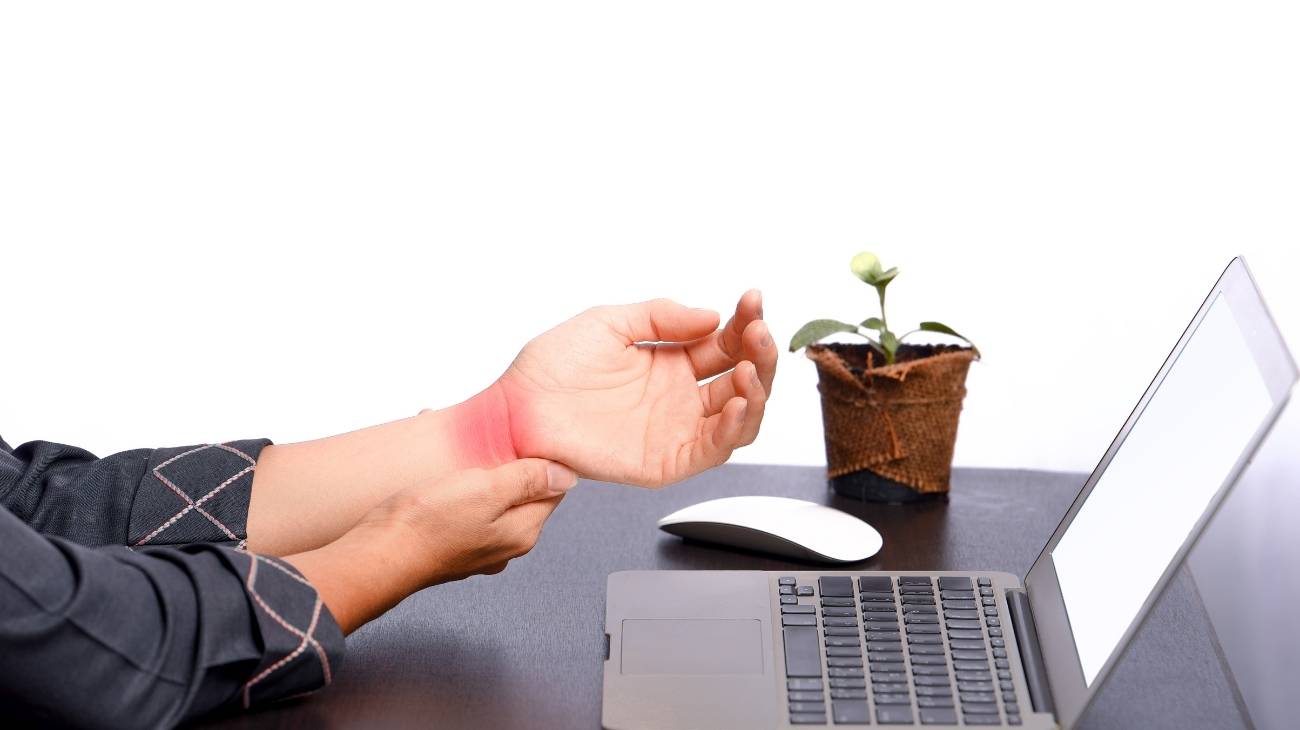
In the event of trauma, injury or knocks, it is very safe to use hot and cold gel packs as a therapeutic complement. However, there are some cases where it could have an adverse effect or present a risk to the individual's condition.
Hence, the importance of knowing how to avoid the dangers and contraindications in the use of hot and cold gel packs and make safe use of them! Fortunately, you don't have to go anywhere else, in this post we tell you all about it.
For whom is heat or cold therapy best suited and what effects does it have?
It is very convenient to know when it is appropriate to apply cold or heat therapies and what effects they have in each case. The use of thermal gel packs is widespread to treat pain, inflammation and diseases such as arthritis. The effectiveness of these therapies against illnesses and different injuries has made their use more and more frequent. However, the difficulty arises when you do not know whether to use cold or heat, even, both temperatures could be useful for some treatments.
Below, in which situations it is very convenient to apply cold or heat:
Acute post-traumatic conditions
Cold therapies are indicated in musculoskeletal or post-surgical orthopaedic trauma. It helps to reduce swelling, pain, haematomas, secondary hypoxia in adjacent tissues, infiltration of interstitial fluid.
However, to obtain a successful result cryotherapy must be combined with elevation and compression of the affected area and compression. Also, it should be applied as soon as possible, considering the degree of cooling and application time.
Post-operative periods
Applying cold 36 hours after surgery helps to reduce pain and swelling, improves sleep quality and recovery time. It is also very suitable to facilitate physiotherapy. Especially in surgeries associated with extremities and maxillofacial.
On the other hand, the heat, although not much analysed, applied in a habitual manner contributes to the reduction of acute and chronic pain, increasing the comfort of the patient.
Conditions with spasticity
Thanks to cold therapy, it is possible to temporarily reduce hypertonia, allowing the patient to perform some movements and activities. The mobility effect could last between 60 to 90 minutes.
Trauma
Cold therapy is indicated as the first emergency applied in trauma to reduce edema through vasoconstriction. Also, because they slow down the activity of the affected cells, lowering the temperature of the area and the metabolism of the tissues. Heat, on the other hand, acts as an analgesic and decontracts the areas that have suffered the blow. In some cases it helps to relieve pain, but it is not indicated in all cases.
However, what is clear is that it increases the elasticity of the tissues, especially in the muscular area. Heat will help the healing process if applied during the first 48 hours. But, considering that the risk of bleeding must have passed, as there will be an increase in blood flow.
Muscle spasm and cramps
Heat therapies contribute to the reduction of muscle spasms and cramps, joint stiffness. This occurs by increasing the distensibility of collagen fibres, blood flow and metabolism. Thanks to this, heat therapies are ideal as a complement to rehabilitation exercise to avoid risks in the injury.
Fever
Cold therapy is indicated for fevers, as long as they are generated by infection, neurogenic or surgical causes. They manage to lower the body temperature in a generalised way.
Burns
In the event of a slight or superficial burn, the application of cold helps to minimise pain and the formation of blisters, preventing the extension of the erythematous area. However, it should be applied early to obtain better results.
Pain relief
Cold has the capacity to act directly on the receptors and fibres that conduct pain. Also, indirectly by reducing the painful swelling caused by the trauma, including muscle spasms and spasticity. Heat is also indicated to relieve pain thanks to the stimulation of endorphins, generating a sensation of relief, increasing the pain threshold. It also has an analgesic effect on low back pain and menstrual pain.
Atopic dermatitis
The itching generates an itchy sensation in the body. Faced with this symptom, the cold acts directly on the sensory receptors. This is why it is indicated in atopic dermatitis and other diseases that trigger this symptomatology.
Inflammatory processes
Thanks to the fact that the destructive enzymes are more active at high temperatures, it makes the cold very effective against acute inflammatory processes. Some pathologies where this symptom is present are bursitis, arthritis, tendinitis, rheumatism in outbreak, among others. Cold therapies will help to alleviate the symptoms of the inflammation, and will delay the toxicity and its extension.
Acute and subacute arthritis
Osteoarthritis is considered one of the most common forms of arthritis, affecting the hands, hips, shoulders and knees. The most common symptoms are pain and swelling, where heat or cold therapy will help improve the symptoms. The heat effect helps to improve circulation and relax the muscles. Meanwhile, the cold numbs the area of pain and reduces inflation, blocking nerve impulses and contracting blood vessels to the joint.
Arthroplasties and stents
With total knee replacement and stenting, cold therapy will help reduce pain and blood loss. It also helps to improve mobility after surgery.
Tendinitis
For an acute injury like tendinitis that causes inflammation, swelling and pain, applying cold is an excellent option, as long as the injury is recent. Focused application of cold will numb the painful area and cause the blood vessels to contract, reducing swelling.
Fractures
Cryotherapy is indicated after a fracture, ankle injury or sprain. Pain is reduced and so is drug consumption, combined with exercise therapy that will work very well for the patient's recovery.
Bestseller
In what type of diseases can the application of cold or heat be contraindicated?
Although heat and cold therapy are not an effective treatment for any disease, they are a therapeutic complement to help in the successful recovery of a disease. Therefore, when in doubt, it is necessary to know what type of illness may be contraindicated so as not to aggravate the patient's condition. Let's see:
Contraindications to the application of cold
In the following section, we would like to clarify what kind of diseases there are contraindications to the application of cold:
- Hypertension: Cold is contraindicated in hypertensive people because it would put their health at risk. The blood vessels could react to the abrupt change in temperature as stress responses generated by the cold: Especially in people over 65.
- Joint stiffness: Reducing temperature increases joint stiffness because it affects collagen tissue.
- Decrease or loss of sensitivity: Although cold has an analgesic effect due to the decrease in sensitivity, it is contraindicated for people who suffer from decreased or loss of sensitivity, because it would decrease it even more.
- Vegetative dysfunctions: The expected therapeutic effects may not be effective, as some circulatory responses depend on the sympathetic nervous system.
- Conditions that occur with vasospasm: Especially, those who suffer from Raynaud's disease. It is an absolute contraindication due to the narrowing of the blood vessels that the individual will suffer when coming into contact with the cold.
- Hypersensitivity to cold: Cold therapy cannot be applied to those who suffer from this abnormal sensitivity to contact with cold temperatures or cold environments.
- Hives or allergy to cold: This skin disorder when coming into contact with cold makes cryotherapy contraindicated.
- Thromboangiitis Obliterans: At least 50% of patients suffering from this disease have increased sensitivity to cold or Raynaud's disease.
- Assessment of muscle strength: Those who require this assessment cannot be done after cryotherapy. It could have adverse effects caused by temporary changes in the muscle.
- Peripheral vascular disorders: This disorder is associated with Raynaud's disease, where hands and feet suffer spasms when in contact with the cold.
- Arteriosclerosis: This disease is associated with peripheral vascular disorders and, consequently, with Raynaud's disease, so contact with the cold is contraindicated.
- Ischemia: Cold reduces blood pressure, heart rate and metabolism, being counterproductive in case of ischemia.
- Cryoglobulinemia: This condition is associated with rheumatoid arthritis, leukemias, lupus erythematosus and multiple myeloma, where the patient could suffer a blockage of the vessels when having contact with cold. This, as a consequence of the precipitation of abnormal proteins and cryoglobulins in the blood.
- Skin lesions: When skin lesions have developed inflammatory effects as a consequence of chronic diseases, cold is contraindicated.
Heat application contraindications
Now, we want to talk to you about the contraindications of heat application for the following diseases:
- Injuries: The application of heat before the first 24 hours of the injury is contraindicated, as it could increase the blood flow and encourage bleeding.
- Alterations in sensitivity: Those suffering from these alterations in thermal and painful sensitivity, contact with heat is contraindicated.
- Cardiopathies: On coming into contact with heat, an alteration in cardiovascular health is generated, being contraindicated in patients with cardiopathies.
- People with diabetes: Heat could generate dehydration and consequently an increase in blood glucose. Also, it could generate a hypoglycemia due to the increase of the speed of insulin absorption. Other complications include damage to blood vessels and nerves.
- Infectious processes: When faced with infectious processes, inflammations caused by osteomyelitis, arthritis or local infectious disorders due to cellulitis, heat is not indicated, as it contributes to the proliferation of bacteria, viruses or other microorganisms.
- Neoplasms: Heat may increase the size of malignant/benign tumours and neoplasms.
- Glaucoma: A tributary ophthalmological emergency could be triggered with possible surgical treatment as a consequence of the increase of eye pressure due to contact with heat.
- Severe hypotension: Lowering blood pressure by contact with heat could generate a potentially fatal condition for the individual.
- Active haemorrhage: Heat favours increased haemorrhage and is therefore contraindicated in this condition.
- Liver failure: Contact with heat could trigger a multiorganic diffusion, including liver failure, generating serious complications.
- Acute inflammation: The application of heat to a lesion could generate an increase in inflation and greater pressure on the tissues.
- Renal problems: A renal evaluation is necessary before applying heat to avoid sweating, sedation and muscular relaxation that could aggravate the health of the individual.
- Active skin disorders: Heat increases the risk of infection from skin infections, e.g. fungi.
- Active collagenopathies: Heat therapy makes the collagen fibres more extensible, being counterproductive when the individual suffers from active collagenopathy due to an excess of collagen.
- Anaesthesia or skin hypesthesia: Heat causes an opposite effect to cold by reducing local vasoconstriction or hypesthesia, contributing to the generation of inflammation and oedema after an injury.
What are the risks and precautions to be taken before using hot/cold gel packs?
Before using hot and cold gel packs, it is important to know the risks and precautions to be taken into account, and we will tell you right now:
Dangers of cold
In the following list we will tell you the main risks that exist when applying cold gel packs:
- Avoid application directly to wounds. This contraindication is due to the fact that the wound healing process could be prevented by contact with low temperatures.
- Avoid application on superficial areas of nerve formations. Especially for a very long time due to possible neural problems such as neuropraxia or axonotmesis.
- Ice burns. Although they are not very frequent, it is important to take them into account. Especially when the time of application suggested by the specialist has been exceeded, or when it has been indicated under contraindication to risks in patients with disorders associated with decreased skin sensitivity.
- Fatty necrosis and freezing phenomena. Also, its appearance is very unlikely, but it must be taken into account that its appearance is due to the application of cold in risks of contraindication and excessive time.
- Aversion to cold. Those who present intolerance to this thermal agent cannot use cold therapies.
- Over exposure to cold. This condition will increase capillary permeability by a significant percentage, causing an increase in blood viscosity in capillaries and, consequently, production of occlusive masses.
Dangers of heat
Applying heat in a focused area or in a general way should also be done with strict precautions to avoid risks. Some of them are:
- Burns. When heating the bag of cold gel in humid conditions, it should be taken into account that the increase in temperature cannot be controlled, and therefore contact with the skin could generate local burns. Our recommendation is not to exceed 58º, and if it has been exceeded, you should let it cool down and heat it up again.
- In case of inflammation. There is a contraindication to the application of heat when the injured area is red, inflamed or hot. In this case, it is best to apply cold.
- In case of muscular and joint contusions. Heat should be applied only when the acute phase has been overcome, i.e. after 48 - 72 hours. Initially, the recommendation is to apply cold.
F.A.Q: Frequently Asked Questions
In the next segment we will answer the most frequently asked questions from users on the Internet about the correct use of hot and cold gel packs: