- What are involuntary muscle cramps or spasms?
- What are the most common types of muscle cramps?
- Best products for muscle cramps
- What are the causes of involuntary muscle spasms?
- Main symptoms associated with muscle cramps
- How to relieve the pain and improve the symptoms of muscle cramps?
- What are the most effective prevention methods for muscle spasms?
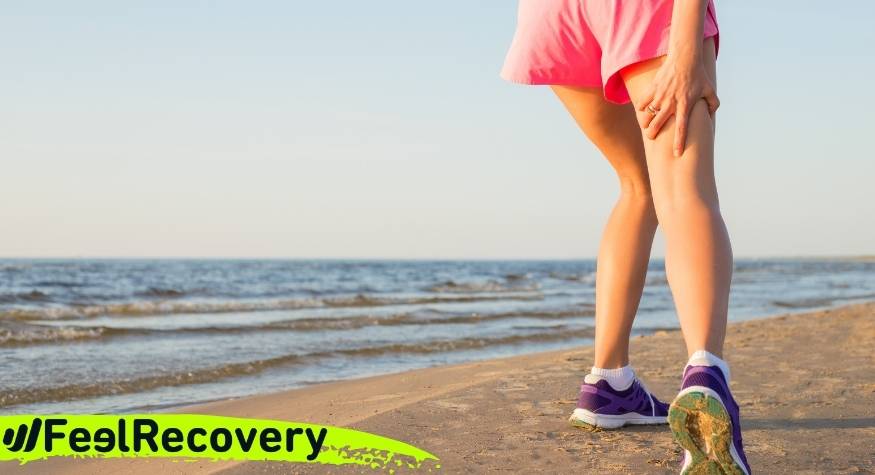
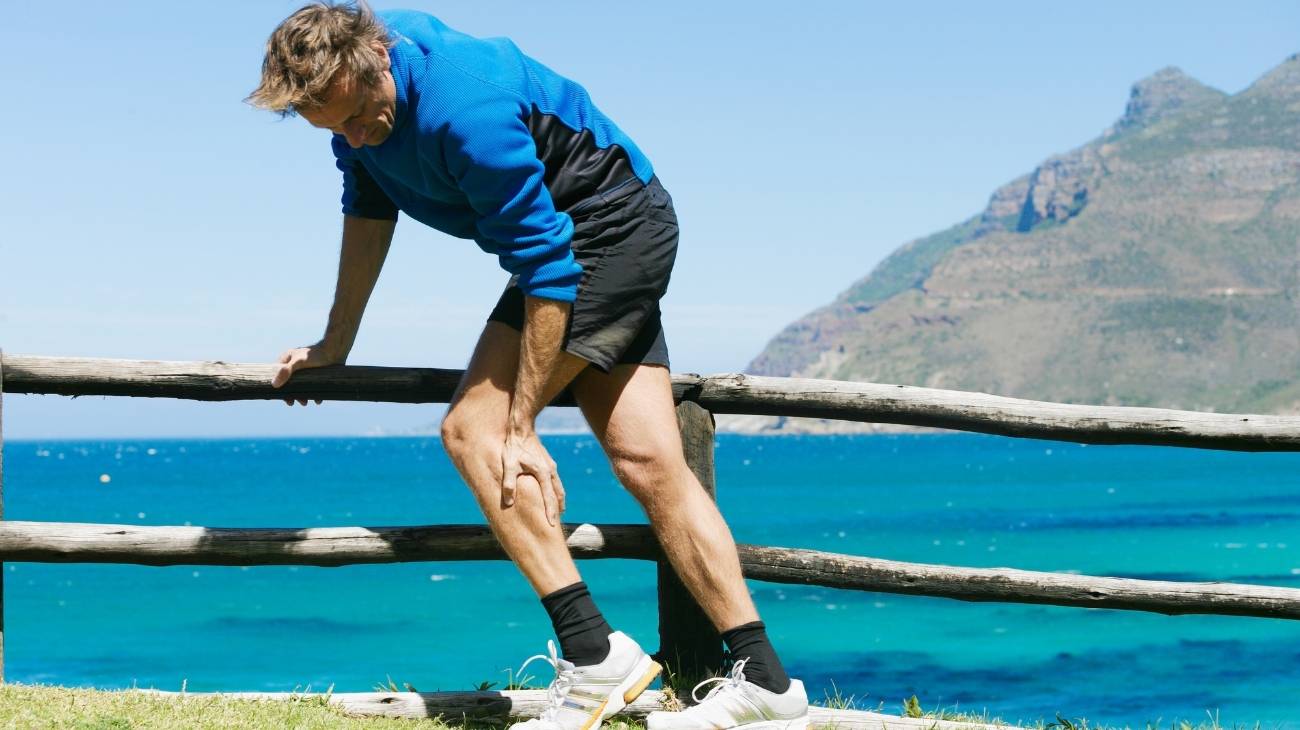
Older and middle-aged adults, as well as young people, can be affected by muscle spasms. Muscle spasms usually occur in different parts of the body and tend to produce a nagging pain that can last for a prolonged period of time and disrupt the patient's regular activities.
Therefore, it is essential for people to know more about what involuntary spasms in the body's musculature are and what are the different types that can be distinguished. In addition, it is appropriate to know each and every cause of this condition, as well as its symptoms, recommended treatments and prevention methods for such contractions.
What are involuntary muscle cramps or spasms?
Basically, muscle cramps or spasms are defined as contractures that occur in a muscle or a group of muscles and do not allow them to relax. As such, they are characterised by a sudden, involuntary and abrupt contraction that makes it temporarily impossible to use the affected muscle and can last for several minutes (even more than 15 minutes).
In this sense, when a muscle cramp occurs, the muscle or muscles that have been affected automatically stiffen and bulge, to the point of producing great discomfort that is translated into pain and swelling in the affected area. However, although it is a painful condition, it is not considered serious.
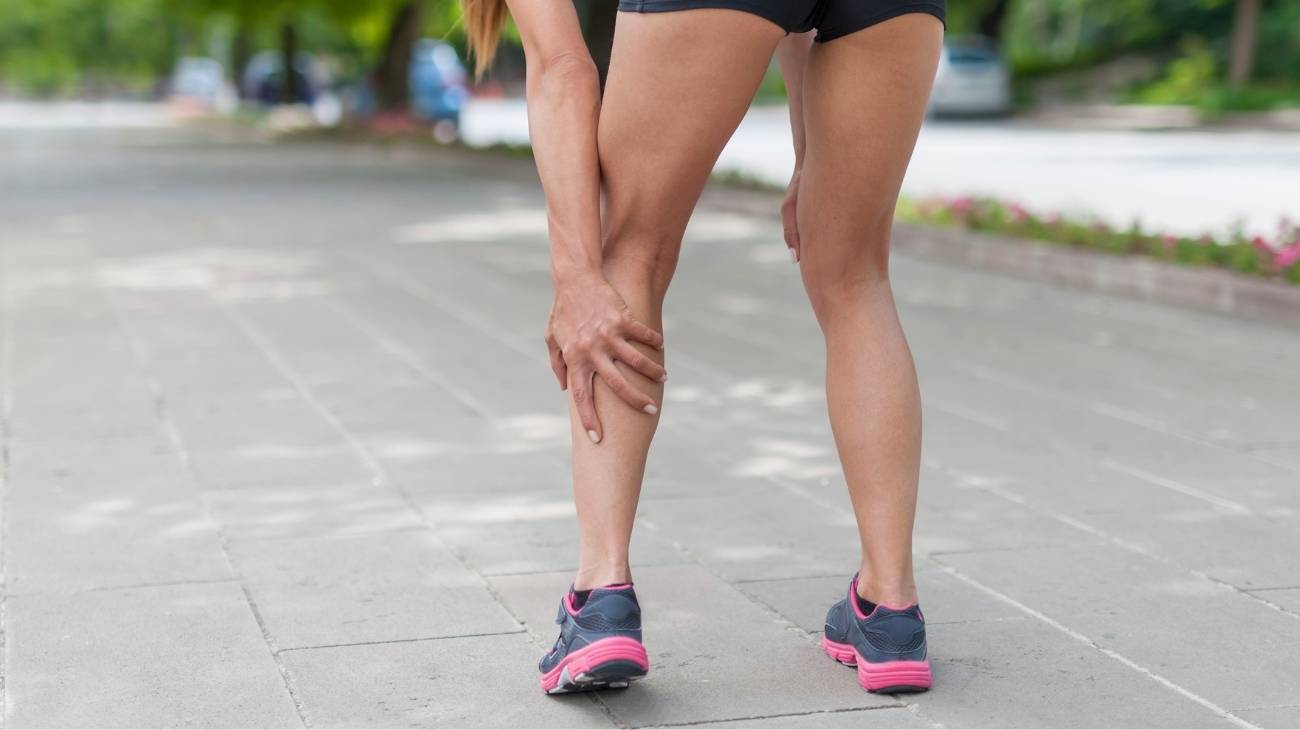
In most cases, this kind of spasm usually affects three different muscle groups, which are
- The quadriceps or the front of the thigh.
- The hamstrings or the back of the thigh.
- The calves.
However, it should be noted that muscle contractions can occur in any muscle in the body, as long as it is contracted and unable to relax.
What are the most common types of muscle cramps?
Since sudden cramps can occur at certain times or in specific muscles, there are several types of muscle spasms that patients are interested in knowing about in order to know what their condition is.
As a result, we highlight below what cramps consist of depending on the moment at which they occur and the type of weakened muscle:
Depending on the moment of the cramp
It is no secret that the most basic reason why cramps appear in the muscles is due to exercise. Therefore, one of the main classifications of this type of spasm is based on the time at which the ailment occurs. Either while the patient is engaged in physical activity or after exercise:
- Spasms during exercise: It is possible that, at the time of exercise, the affected individual makes an excessive effort to increase the intensity of their activity or makes a sudden movement that, as a consequence, causes the accumulation of metabolic waste within the muscle fibre. This automatically initiates involuntary contraction in the affected area.
- Spasms after exercise: If, once the person exercises, stretches incorrectly, the body ends up dehydrated or accumulates a lot of sweat after finishing the physical activity, the muscle fibre will be affected and this will also be another cause of the spasm.
According to the type of musculature affected
This classification proposes that muscle contractions also tend to be generated by the type of musculature receiving the temporary trauma. In such a case, the types of muscle cramps that exist depending on the type of musculature affected refer to:
- Nocturnal cramps: These are the most frequent spasms and mainly appear during the night. They occur when the patient's body has low levels of magnesium (hypomagnesaemia) or other minerals that lead to muscle weakness. In addition, nocturnal cramps are also caused by dehydration and decreased blood flow to the muscles.
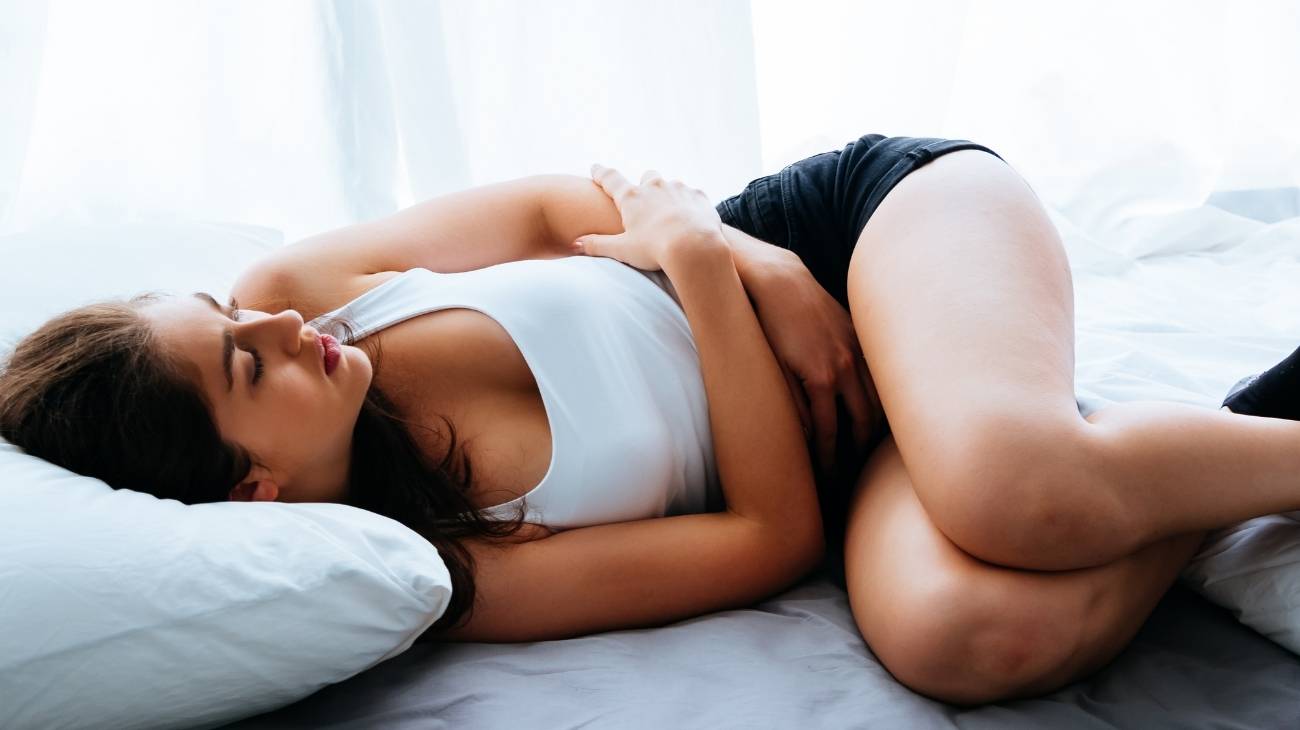
- Smooth muscle cramps: In this case, they are the spasms that affect women before or during their menstrual cycle. Since, the period tends to affect the smooth muscle which is a muscular tissue located in the organs of the abdominal and pelvic cavity. Thus, it is a type of spasm that leads to symptomatic contractions.
- Musculoskeletal cramps: This is an intense and painful spasm affecting the thighs, calves and arches of the feet after a period of physical activity. This means that these cramps are associated with strenuous and exhausting activity. Thus, they are characterised by occurring immediately after the patient has exercised.
Best products for muscle cramps
Bestseller
-
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
£20,95 -
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
£20,95 -
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
£20,95 -
2 Thigh Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
£20,95 -
2 Thigh Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
£20,95 -
2 Thigh Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
£20,95 -
Back Support Belt (Black)
£39,95 -
Back Support Belt (Green)
£39,95 -
Back Support Belt (Pink)
£39,95 -
Microwave Wheat Bag for Back Pain Relief (Extra Large) (Hearts)
£24,95 -
Microwave Wheat Bag for Back Pain Relief (Extra Large) (Oxford)
£24,95 -
Microwave Wheat Bag for Back Pain Relief (Extra Large) (Sport)
£24,95 -
Microwave Wheat Bag for Neck Pain Relief (Hearts)
£20,95 -
Microwave Wheat Bag for Neck Pain Relief (Oxford)
£20,95 -
Microwave Wheat Bag for Neck Pain Relief (Sport)
£20,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Hearts)
£20,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Oxford)
£20,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Sport)
£20,95 -
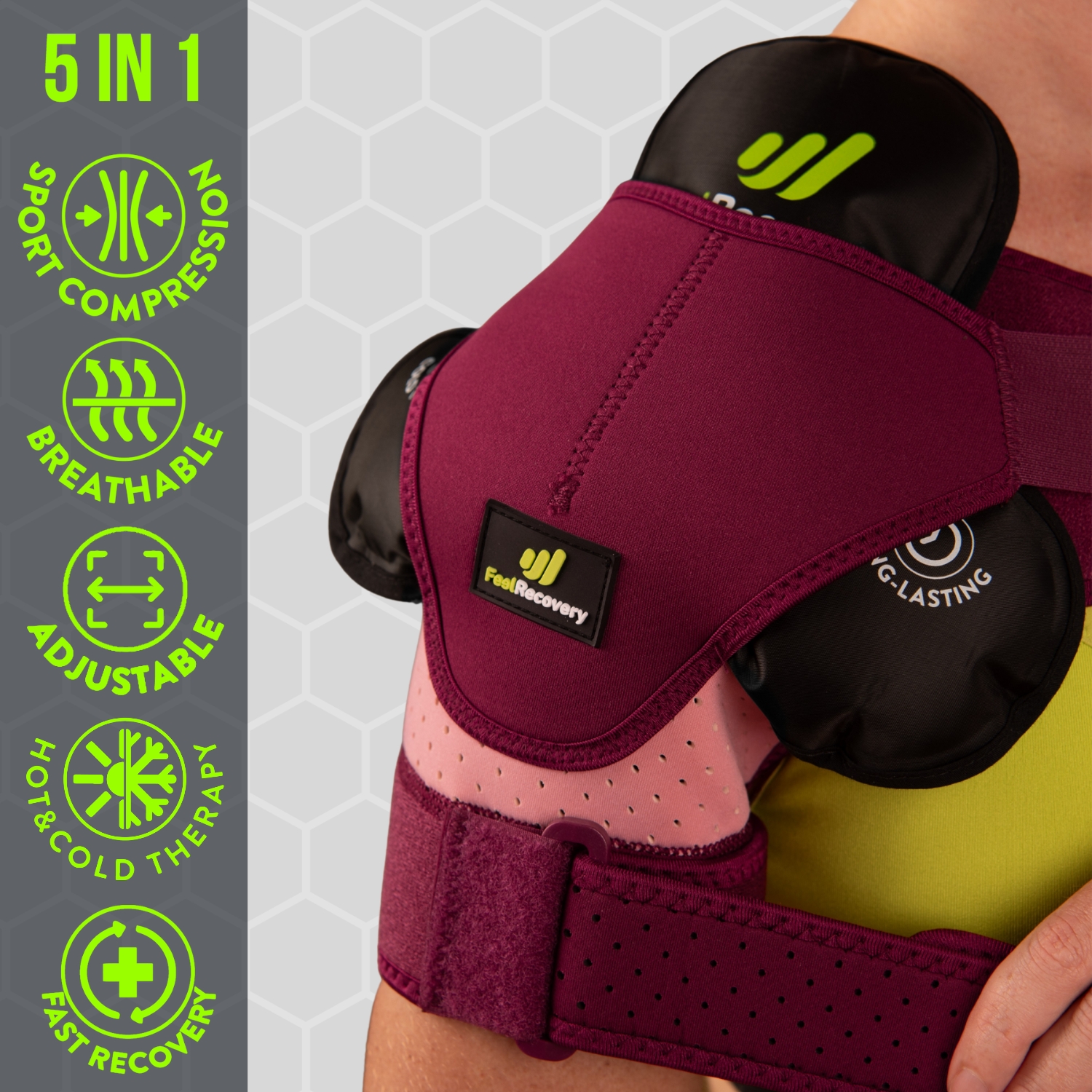
Shoulder Support Brace (Green)
£24,95
-
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Black)
£20,95 -
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Green)
£20,95 -
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Pink)
£20,95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Black)
£34,95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Green)
£34,95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Pink)
£34,95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Black)
£24,95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Pink)
£24,95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Black)
£34,95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Green)
£34,95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Pink)
£34,95 -
Sport Compression Socks (1 Pair) (Black/Gray)
£20,95 -
Sport Compression Socks (1 Pair) (Green/Navy)
£20,95 -
Sport Compression Socks (1 Pair) (Pink/Bordeaux)
£20,95
What are the causes of involuntary muscle spasms?
It is true that this type of sudden and temporary cramps occur when the muscles are overloaded or injured. However, beyond knowing this, most people are interested in knowing the reasons or principles by which such spasms occur in an individual.
Therefore, the most relevant causes are listed below:
- One of the main causes of muscle spasms is undoubtedly dehydration or the fact of doing physical activity without having ingested the fluid required by the body.
- When muscles are poorly supplied with blood or get an inadequate blood supply, cramps also occur.
- Low levels of minerals such as magnesium, calcium and potassium are a source of involuntary contractions in these areas of the body.
- Stress and anxiety also cause temporary spasms, especially in the neck area.
- Due to reactions to certain drugs or medications, many people suffer from this muscle ailment.
- Other risk factors include certain conditions such as pregnancy, dialysis, and certain nervous, thyroid or liver disorders.
- Smoking tends to generate this type of cramp, as smoking contributes to direct damage to the muscles (especially those located in the legs).
- Poor diet or certain nutritional deficiencies are also factors associated with the production of muscle spasms.
- If there is trauma to a nerve connected to a muscle, involuntary cramps are likely to appear constantly.
Main symptoms associated with muscle cramps
Whenever there is a muscle spasm, a series of signs or indications are externalised that alter the organism to reveal the ailment generated by these contractions, naturally. By means of this, the patient will be able to recognise what he or she is suffering from and have a better perception of the pathological state into which he or she has entered.
It is essential to know what symptoms occur when there are spasms in the muscles and here, we point out each one of them:
- Contortion and stiffening in the muscle(s) afflicted by the cramp, suddenly and uncontrollably.
- Redness, swelling and skin changes in the affected area. It is even possible that muscle tissue may appear under the skin.
- A sudden, sharp pain in the muscle that may last for several minutes (in the worst cases, 15 minutes or more).
- Great tenderness in the muscle that has been traumatized by the spasm for 24 hours after the spasm.
- Difficulty in moving the area where the contracted muscle is located normally. Whether it is the foot, leg, neck, hand, etc.
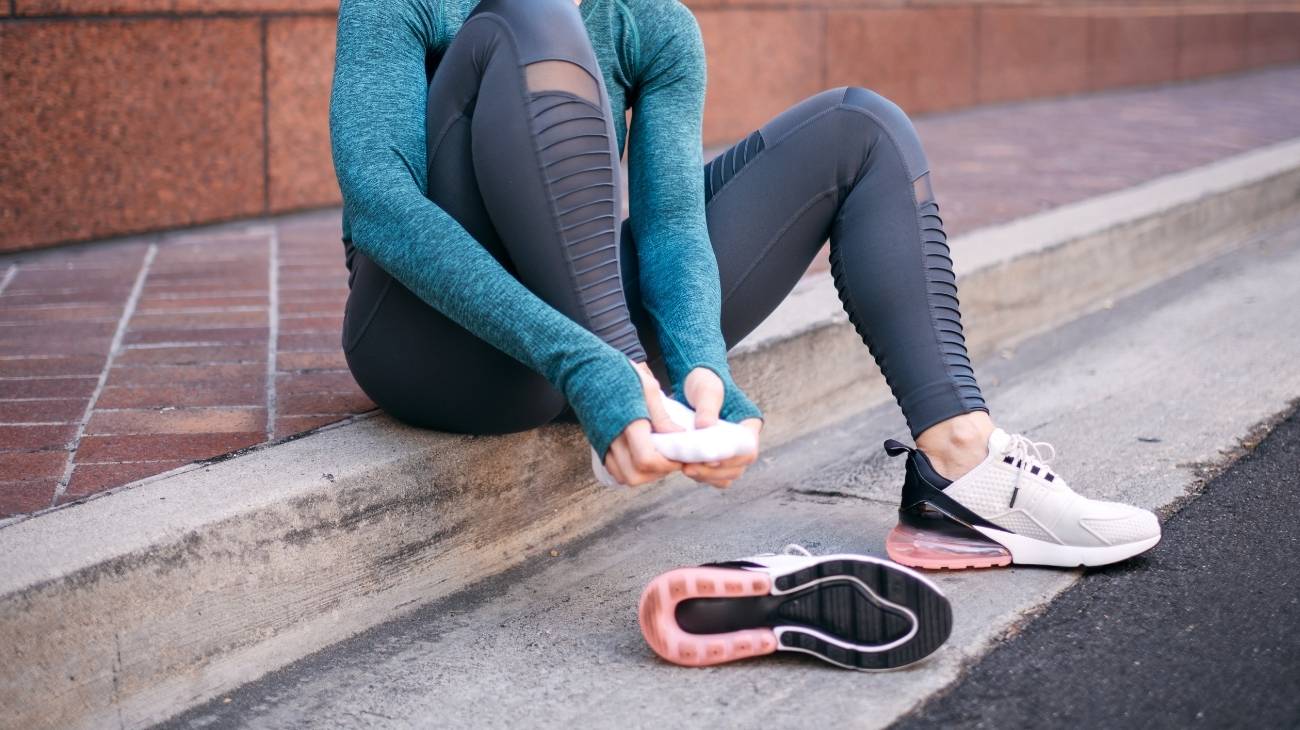
How to relieve the pain and improve the symptoms of muscle cramps?
Individuals who suffer from cramps in their muscles can resort to certain therapies, treatments, food supplements and drugs indicated to act against the intense pain generated by these involuntary spasms.
Given that, alternative medicine guarantees different techniques that help to relieve the discomfort effectively and here, we highlight which are each of them:
Alternative and complementary therapies
There are various therapies or therapeutic techniques that help to minimise the symptoms associated with muscle pain caused by cramps, and these are the following:
- Compression therapy: This is a medical therapy that uses an elastic device to exert controlled pressure on certain areas of the body that require increased blood flow to function properly. Thus, patients who suffer from muscle contractions in their limbs or any other area of the body may use knee, elbow, ankle or thigh compression braces that squeeze the walls of the veins to attenuate or prevent the symptoms caused by these spasms.
- Massage therapy: Therapeutic massages are also effective in reducing the pain and stiffness that occurs during and after muscle cramps. In addition, they are ideal for improving circulation in any part of the body. In this case, the affected area is simply rubbed and rubbed to relax it and relieve the ailment.
- Acupressure therapy: This is a treatment created by traditional Chinese medicine that focuses on stimulating various points on the human body by exerting pressure on certain areas with the help of the expert's fingers or elbows. In this way, by triggering a healing response through the soles of the feet, the palms of the hands and the articular pavilion, it manages to soothe pain in patients affected by involuntary contractions.
- Thermotherapy: Undoubtedly, heat is a great ally to moderate the pain generated by a muscle cramp and for this reason, it is recommended to resort to thermotherapy, which applies a temperature higher than that of the body itself. In this way, it naturally manages to provide an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, sedative and relaxing effect on the affected person, whether in solid, gaseous or semi-liquid form.
- Natural remedies using plants: Natural remedies are also distinguished as an optimal complementary therapy to counteract the symptoms of muscle spasms. They tend to reduce swelling in certain parts of the body, promote blood circulation and alleviate ailments. In this case, infusions of horsetail, dandelion, romaine, horse chestnut, etc. are recommended.
- Meditation and relaxation: You can meditate to achieve a state of relaxation that allows you to be more aware of what is happening in your body, as well as to understand your ailments and learn to control them. In this way, it will be easier to find the necessary relief when muscle spasms occur. Keeping in mind that these relaxation techniques also allow you to release tension and relieve anxiety.
- Aromatherapy: Some essential oils such as lavender, thyme, fennel and cayenne allow you to soothe the pain generated by spasms, as well as obtain a high level of relaxation through their aromas. Thus, from them, you can implement the aromatherapy that emerges as an alternative medicine based on the use of aromatic materials to achieve an excellent physical and psychological well-being that relinquishes any discomfort.
- Acupuncture: With the insertion of fine needles into the human body, acupuncture has the ability to improve the symptoms of cramps in the muscles. Since, following several keys of the traditional Chinese medicine, by piercing specific areas of the body, this therapy manages to increase the circulation of the blood to attenuate the ailments that appear in the muscles due to these sudden contractions.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: If you implement certain healthy habits in your daily life, it will also be very easy to improve the symptoms of muscle contractions and soothe the pain caused by them. These include: drinking water and staying hydrated at all times, eating healthy foods that are rich in minerals (such as magnesium and potassium), avoiding a sedentary lifestyle, exercising without overdoing it or overwhelming the muscles, stretching before and after any physical activity, etc.
Dietary supplements
Dietary supplements or food supplements are all those products made to complement a healthy diet, given that they contain optimal amounts of vitamins, minerals, enzymes, fatty acids and amino acids among their ingredients. Therefore, they are able to provide nutrients to the body in order to provide a feeling of wellbeing when following a certain treatment.
Consequently, although they cannot be used as substitutes for conventional foods, they are essential for integrating healthy lifestyle habits. Thus, many of them are indicated to attenuate the symptoms generated by muscle cramps and even prevent these spasms from occurring in patients.
In such a case, it is recommended to resort to the following dietary supplements in order to achieve relief from this ailment:
- Magnesium: Since one of the main causes of these contractions is low levels of magnesium in the body, it is ideal to eat foods that provide this nutrient. This helps to reduce and prevent the pain and discomfort produced during a muscle cramp. As if that were not enough, it also has the ability to reduce anxiety and stress, which tend to worsen the condition in question. Some foods rich in magnesium are: spinach, avocado, chickpeas, lentils, quinoa, wholemeal bread, nuts, dark chocolate, etc.
- Omega 3: Omega 3 is defined as an essential oil that produces an anti-inflammatory effect in the body and strengthens the blood vessels, thus providing great relief when cramps occur in any of the body's muscles. In addition, this supplement provides the body with a lot of energy, improves the heart, lungs, endocrine system and immune system. You can find it in: fish, milk, eggs, yoghurt, oatmeal, nuts, olive oil, etc.
- Potassium: This is an essential mineral for the body to function properly, as it helps to establish water balance and improve the functioning of the nervous and muscular systems. Thanks to this, as well as preventing cramps in the muscles, it also manages to reduce the pain generated by this condition in patients. Because of its benefits, the WHO recommends consuming 3,510 grams of potassium every day. This dietary supplement can be obtained from: bananas, papaya, kiwi, broccoli, spinach, tomatoes, meat and fish, dairy products (milk and yoghurt), etc.
- Calcium: This is considered an extremely important mineral because it is involved in various enzymatic reactions, as well as in the regulation of muscle contraction and bone mineralisation. It is therefore essential to ensure optimal functioning of nerves, muscles and bones. It thus improves the symptoms of muscle spasms and ensures good blood circulation through the vessels throughout the body. To consume calcium, you can eat foods such as cheese, milk, yoghurt, broccoli, Chinese cabbage, seafood, nuts (hazelnuts or almonds), dried figs, raspberries, oranges, etc.
- Vitamin B1: This is a food supplement that is mainly used to treat magnesium deficiency in the body of individuals and, as a result, tends to minimise the discomfort caused by muscle contractions. It also optimises brain function, improves the nervous system and provides great energy. Among the main foods that provide vitamin B1 are: tuna, trout, eggs, peas, pulses, seeds, nuts, wheat germ, rice, etc.
Medications
In many cases, muscle spasms disappear on their own in a short time and are not considered a serious health problem. However, when the pain caused by this condition is very intense and prolonged, it is advisable to visit a specialised doctor.
Especially if any of the following incidents occur: The cramp lasts for a long time, does not improve with stretching or hydration, occurs constantly, is severe, causes muscle weakness, is accompanied by redness, swelling or a sensation of heat.
Thus, the trained professional will be able to examine you personally, evaluate the different factors involved in the occurrence of these spasms (history, age, state of health, type of cramp, tolerance to medication, etc.) and, based on this, will determine which treatment you need. For this reason, self-medication is not recommended because the side effects could be serious (nausea, diarrhoea, intoxication, gastritis, drowsiness, addiction, dependence, cardiac arrest, etc.).
What are the most effective prevention methods for muscle spasms?
Fortunately, it is possible to prevent muscle cramps, regardless of the different causes for which these contractions may occur. Because, with certain habits, the body will gain the ability to prevent this ailment that often negatively affects the daily life of patients.
Therefore, to conclude, we would like to let you know which are the most effective prevention methods to expel cramps from your muscles:
- Exercise regularly: If you incorporate physical activity into your daily routine, progressively and without overloading your muscles, you will be less likely to suffer from muscle spasms. To do this, you can start with short distances and gradually increase the intensity and time of the exercise to avoid overdoing it.
- Warm up properly before any physical activity: In order to avoid muscle injury and contractures, it is essential to warm up properly before any exercise. This reduces the risk of damage to the muscle fibres and prevents sudden spasms.
- Learn to stretch your muscles: By nature, muscle stretching exercises help to prevent contractures in these areas of the body. In this case, you should focus on achieving constant movement and ideal effort through stretching, without trying to push the muscles to their limits. Importantly, it is appropriate to include stretching in your daily routine (not just when you exercise).
- Keep your body hydrated: By doing so, you can avoid any degree of dehydration, which is one of the most notable causes of muscle spasms. Therefore, drink the recommended amount of water per day (2.7 litres for women and 3.7 litres for men).
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet: It is important to consume healthy food together with certain dietary supplements rich in minerals and vitamins that help the body to hinder the onset of muscle contractions. This helps the body to function properly and thus prevents involuntary hardening of these areas.
- Practice relaxation methods: You can also use yoga, meditation and other relaxation techniques to reduce anxiety and stress which, in a way, cause muscle spasms. While doing these practices, it is important to gently inhale and exhale to provide a state of calmness to the body as a whole and thus ease any tension in the muscles, back and neck.
References
- Miller, T. M., & Layzer, R. B. (2005). Muscle cramps. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, 32(4), 431-442. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mus.20341
- Minetto, M. A., Holobar, A., Botter, A., & Farina, D. (2013). Origin and development of muscle cramps. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews, 41(1), 3-10. https://journals.lww.com/acsm-essr/fulltext/2013/01000/origin_and_Develop_of_muscle_cramps.3.aspx
- McGee, S. R. (1990). Muscle cramps. Archives of Internal Medicine, 150(3), 511-518. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/article-abstract/612935
- Bergeron, M. F. (2008). Muscle cramps during exercise-is it fatigue or electrolyte deficit?. Current Sports Medicine Reports, 7(4), S50-S55. https://journals.lww.com/acsm-csmr/fulltext/2008/07001/muscle_cramps_during_exercise_is_it_fatigue_or.9.aspx
- Miller, K. C., Stone, M. S., Huxel, K. C., & Edwards, J. E. (2010). Exercise-associated muscle cramps: causes, treatment, and prevention. Sports Health, 2(4), 279-283. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1941738109357299
- Schwellnus, M. P. (2009). Cause of exercise associated muscle cramps (EAMC)—altered neuromuscular control, dehydration or electrolyte depletion?. British journal of sports medicine, 43(6), 401-408. https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/43/6/401
- Schwellnus, M. P. (1999). Skeletal muscle cramps during exercise. The Physician and Sportsmedicine, 27(12), 109-115. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3810/psm.1999.11.1116
- Jung, A. P., Bishop, P. A., Al-Nawwas, A., & Dale, R. B. (2005). Influence of hydration and electrolyte supplementation on incidence and time to onset of exercise-associated muscle cramps. Journal of Athletic Training, 40(2), 71. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1150229/
- P. Schwellnus, M., Derman, E. W., & Noakes, T. D. (1997). Aetiology of skeletal muscle ‘cramps’ during exercise: a novel hypothesis. Journal of sports sciences, 15(3), 277-285. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/026404197367281
- Diener, H. C., Dethlefsen, U., Dethlefsen-Gruber, S., & Verbeek, P. (2002). Effectiveness of quinine in treating muscle cramps: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentre trial. International journal of clinical practice, 56(4), 243-246. https://europepmc.org/article/med/12074203