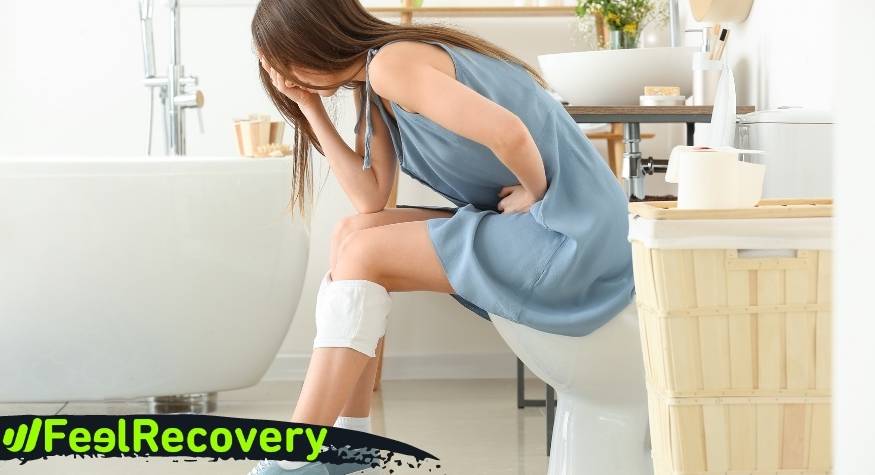
Pain from swollen haemorrhoids is very common in most people. It is not usually a serious health problem, but it does cause a lot of discomfort and pain. Because they are rarely diagnosed and treated, they tend to progress and grow in size.
Although there are many treatment options to improve them, they usually respond very well to gel pack cold therapies. If you would like to know more about these therapies to relieve the pain of swollen haemorrhoids, be sure to read the following information.
What are the causes and origin of inflamed haemorrhoid pain?
Hemorrhoids are a group of veins that are part of the circulation in the area of the rectum and anus. Inflammation of these veins gives rise to haemorrhoidal disease and they are commonly called "piles".
Haemorrhoidal disease is characterised by congestion, inflammation, displacement and prolapse of these veins to the outside of the anus. It is a very common pathology and although it is not a serious disorder, it generates a lot of discomfort and pain. It tends to affect men and women equally frequently between the ages of 40 and 60. However, in pregnant women the rate of occurrence increases due to the poor circulation characteristic of pregnancy.
The most frequent clinical manifestations are usually:
- Discomfort and pain: This is the characteristic symptom of haemorrhoids, presenting as a sharp pain in the rectal and anal canal. It occurs mostly during or after bowel movements. When there is severe inflammation the pain can occur at any time and persist over time.
- Anal itching: This is another of the symptoms usually reported by people who suffer from it. It is usually confused with intestinal parasitosis, but its distinction is that it can appear at any time of the day. Some parasites that cause anal itching, however, cause discomfort at night.
- Bleeding from the anus or rectorage: Bleeding is one of the symptoms that often cause concern. It can be visible on paper when cleaning or much more abundant in the form of drops in the toilet.
- Prolapsed or prolapsed haemorrhoids: They appear as a painful lump around the anus. They have a high blood content and if they are not reduced in time they can produce thrombi.
If the appropriate treatment is not received for inflamed haemorrhoids, it can generate other pathologies such as:
- Anaemia: This is the result of constant and excessive bleeding over a long period of time.
- Infections: As it is well known, the area of the year and the rectum have a bacterial flora. If there is a rupture of the haemorrhoids the bacteria can enter and generate infections.
- Anal fistulas: can be generated after an infection in that area, creating an opening from the inside to the outside.
Inflamed haemorrhoids or piles are usually classified as internal and external. Internal haemorrhoids are those that occur in the veins inside the anus. They are the most common and are found 2-4 cm above the anus.
They can become inflamed, bleed, hurt after bowel movements and prolapse. External haemorrhoids are generated around the anus and usually accompany internal haemorrhoids and can generate thrombosed haemorrhoids.
According to their severity they can be classified into four degrees:
- Grade I: In this phase of the disease the haemorrhoids can become slightly inflamed inside. They are not visible on examination.
- Grade II: There is a greater degree of inflammation but the haemorrhoids are still internal. Sometimes they can come out externally but they come back in spontaneously.
- Grade III: These are the haemorrhoids that prolapse, especially with bowel movements. In this case they need to be put back in and it is usually very easy to do so.
- Grade IV: In this phase the haemorrhoids prolapse to such an extent that they remain outside the anus. They are usually very large and painful haemorrhoids.
The main cause of haemorrhoids is increased pressure in the anus and the terminal part of the rectum. This increase in pressure generates a dilation that causes them to swell and protrude downwards and externally. Among the most frequent causes are
- Excessive straining when defecating: Repeated straining during defecation can create pressure at the anus that favours the appearance of inflamed haemorrhoids.
- Chronic constipation: Suffering from chronic constipation can condition the appearance of piles. They are generated by the internal pressure produced by the hardened faecal bolus and excessive straining during defecation. This strain increases the likelihood of inflaming haemorrhoids.
- Chronic diarrhoea: Increased stools can cause increased pressure in the anal region and also irritate haemorrhoids.
- Standing or sitting for long periods of time: Inadequate postures from sitting or standing for long periods of time predispose to a slow venous return. This generates poor circulation in the peripheral veins and in the anorectal region.
- Pregnancy: The weight of the foetus generates greater pressure in the intra-abdominal and pelvic veins which favour the appearance of inflamed haemorrhoids. The excessive pressure of childbirth also causes them to become inflamed.
- Lifting a lot of weight: Performing activities that involve lifting a lot of weight conditions greater pressure in the rectal area and the appearance of inflamed haemorrhoids.
Bestseller
What are the advantages of applying cold to reduce the pain of swollen haemorrhoids?
In essence, piles are dilated, swollen and very painful veins. So to counteract this, the cold is required, which produces very beneficial counter-physiological effects.
Cryotherapy is a very simple treatment. It consists of applying cold to the area of the haemorrhoids to relieve the pain and inflammation. It is one of the least invasive methods, unlike surgeries that generate more discomfort and complications.
Among the benefits of applying cold to the area of the anus, we can highlight:
- Vasoconstriction and reduction of inflammation: The vasoconstriction caused by the cold generates a reduction in blood flow in the area of the anus. As a consequence of this, a loss of heat is generated in the skin and deep tissues. This results in an improvement in inflammation and oedema.
- Reduction of pain and itching: applying cold to the anus region generates a release of chemical mediators. One of these is histamine, which contributes to a significant reduction in pain and itching. In addition, the cold interrupts the pain-spasm-pain cycle by producing a relaxation of the muscles and adjacent tissue.
- Reduction in the size of piles: The vasoconstriction generated by the cold considerably reduces the size of haemorrhoids.
- Simple, practical and economical procedure: The application of cold is one of the simplest methods. You can apply it from the comfort of your home and if it is applied correctly it does not generate any side effects. Besides, it is not invasive and does not require expensive treatments.
How to use cold gel packs to reduce swelling in hemorrhoids?
The application of cryotherapy can be done by placing cold gel packs, compresses, sitz baths, and cold gel packs. The compresses are made by moistening a cloth or towel and putting them in the refrigerator or freezer. When it is cold, it is taken out of the pad and placed on a chair so that people can sit on it.
Sitz baths can be performed by placing cold water in a container that allows the person to sit on it for a few minutes. Ice can be added to the water to help keep the temperature cold for 15 minutes. Also, cold gel packs for hemorrhoids can be used. They are cooled in the freezer or refrigerator and placed on the back of the underwear. This way, you have more contact with the rectal and anal area.
However, we must clarify that our gel packs are not designed to be sat on. For this reason, you should follow these recommendations and you can give a correct and satisfactory use to them:
- Cooling the gel packs: They should only be placed inside the freezer or refrigerator for a minimum of 2 hours. After this time it is necessary to check the correct temperature to touch.
- Place the pad in the affected area: As our packs do not allow sitting on them then the person can lie on their stomach and place it in the gluteal region. Our pads do not require the use of protective covers or cloths for use, they can be used directly on the area. This is due to the protective and soft tissue on one side.
- Make exposure times: The gel packs can be placed for a period of 15 to 20 minutes every 1 to 2 hours. The therapy can be performed for 72 hours to help reduce the symptoms of inflammation. Always remember not to exceed the exposure times because they can generate burns and other skin complications.
- Monitoring the skin condition: While the exposure time is being performed remember to be vigilant of the skin condition. If you notice any change in the colour of your skin, remove it immediately.
- Re-cool the gel pack: When the cold therapy with the gel pack is finished, return it to the freezer or refrigerator. It is important that the gel pack recovers its temperature for the new exposure time.