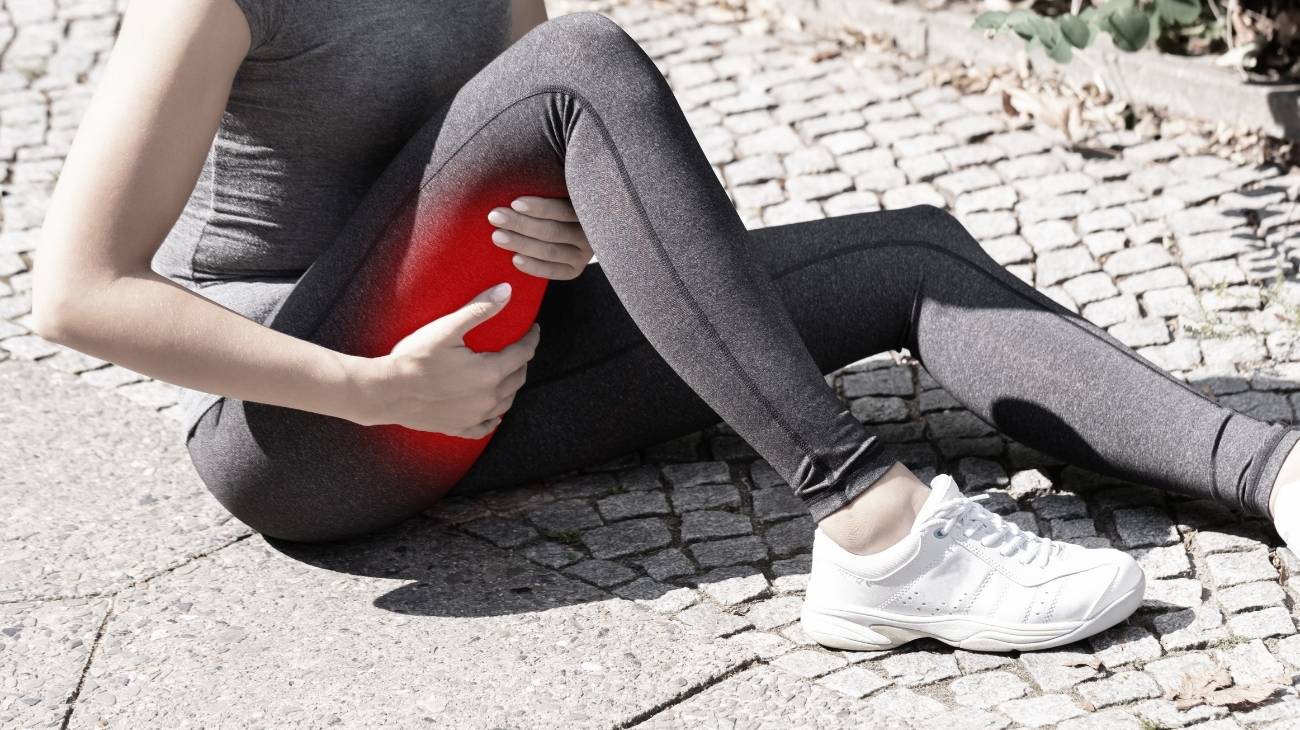
- What are calf and leg muscle strains?
- What are the causes of calf muscle strains?
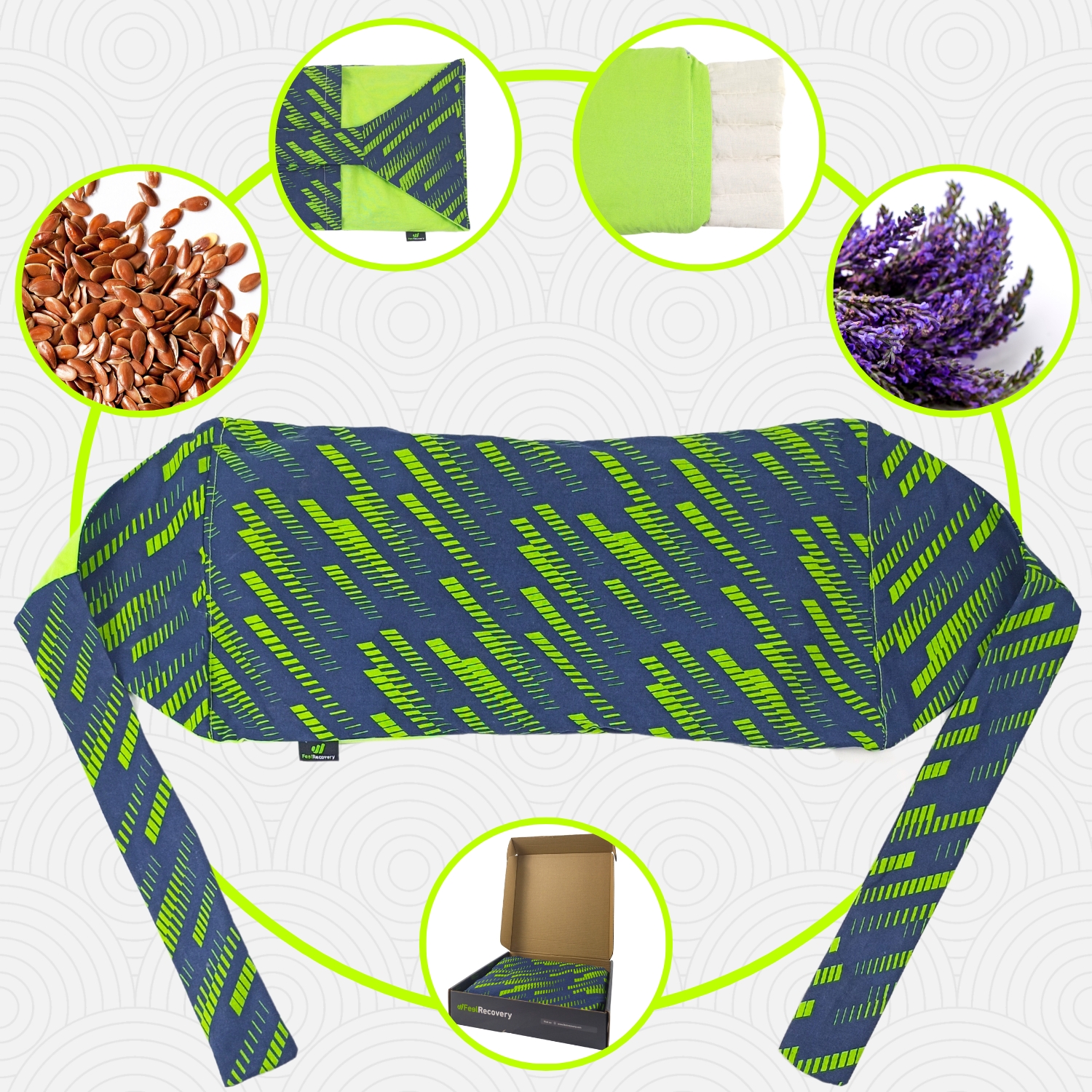
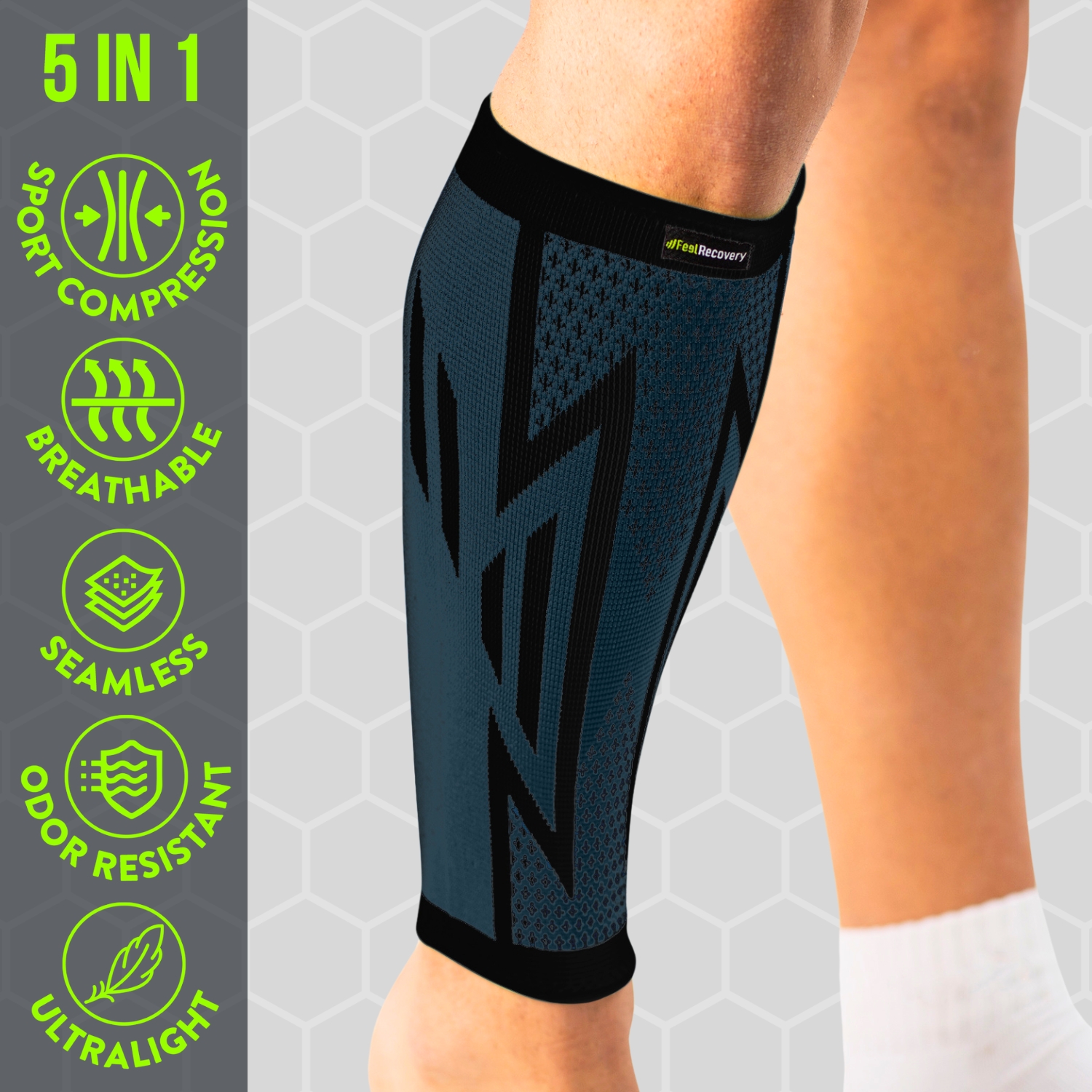
- Best products for calf strains
- Main symptoms associated with calf and leg strains
- How to relieve the pain and improve the symptoms of calf muscle strains?
- What are the most effective prevention methods for calf and leg muscle pulls?
The appearance of symptoms and signs associated with calf and leg muscle strains are the result of involuntary tension in this part of the muscle structure. For this reason, we have prepared this article for you in which you can find out all the facts about this type of muscle strain.
Continue reading until the end because you will find all the information related to the causes of this ailment and the treatments that can be applied for its remission. Finally, we will give you a list of the best tips to avoid these muscle strains in the legs.
What are calf and leg muscle strains?
When performing physical activity or any kind of movement, the calves work by generating metabolites that must be expelled into the bloodstream. If the blood is unable to exchange oxygen and fluids with the muscles, the waste molecules get lodged in this part of the leg and the dreaded muscle pulls arise.
This abnormality leads to involuntary muscle strain or contracture of the person. This leads to stiffness in the muscles, pain, nodules and inflammation. The muscle fibres will cease to be in this dysfunctional situation over a period of weeks. But for this, it is necessary to see a doctor for different treatments, which we will mention in the following paragraphs.
What are the causes of calf muscle strains?
See below the different reasons or factors that influence the appearance of injuries that cause muscle tension in the calves:
- Work or personal concerns: Stress and depression can cause pulled muscles in the soleus and calf muscles. This is due to the large amount of debris in the tissue fibres that is not eliminated by the bloodstream.
- Older people: Age is another factor that can cause muscle pulls in the calf muscles. This is related to the loss of flexibility of the muscle structure.
- Lack of hydration: Water is essential for the soft tissues of the body, especially the muscles. For this reason, not drinking enough fluids can lead to muscle strain in the legs. This is also the case with poor nutrition.
- Inappropriate footwear: Tight shoes and high heels cause the leg muscles to have to exert excessive effort to keep the body in balance. In addition, the calf muscles have to exert more force than normal to lift the foot when walking.
- Cold temperatures: Cold weather can cause muscle strains in the calf muscles, as it is possible to involuntarily keep the muscles in this area of the body contracted.
- Engaging in demanding physical activities: Carrying out actions that require extreme demands on the muscles of the lower limbs can generate a high lactic acid content. This is due to the inability of the blood to exchange nutrients and oxygen with the muscles. In addition, the likelihood of injury can be increased if the calf and leg muscles are not given considerable rest for relaxation.
- Sedentary lifestyle: People who are not active on a frequent basis are more prone to muscle strain injuries in the legs. This is caused by the level of stiffness of the muscles in this affected area, which when doing any kind of task are overdemanded because they are not used to being active.
- Low potassium levels: Nutrients such as potassium, magnesium and sodium are important for maintaining flexibility in the muscles. For this reason, a lack of any of these elements in the body can lead to pulled muscles.
- Lack of flexibility: Stretching and warming up beforehand are necessary to keep the leg and calf muscles in good condition. If these types of activities are not carried out prior to any sport or work practice, the chances of a muscle contracture increase.
- Repetitive movements: The practice of activities or tasks that require repeated and prolonged movement of the leg and calf muscles can cause an injury to them. This will lead to muscle strain in this part of the body.
Best products for calf strains
Bestseller
-
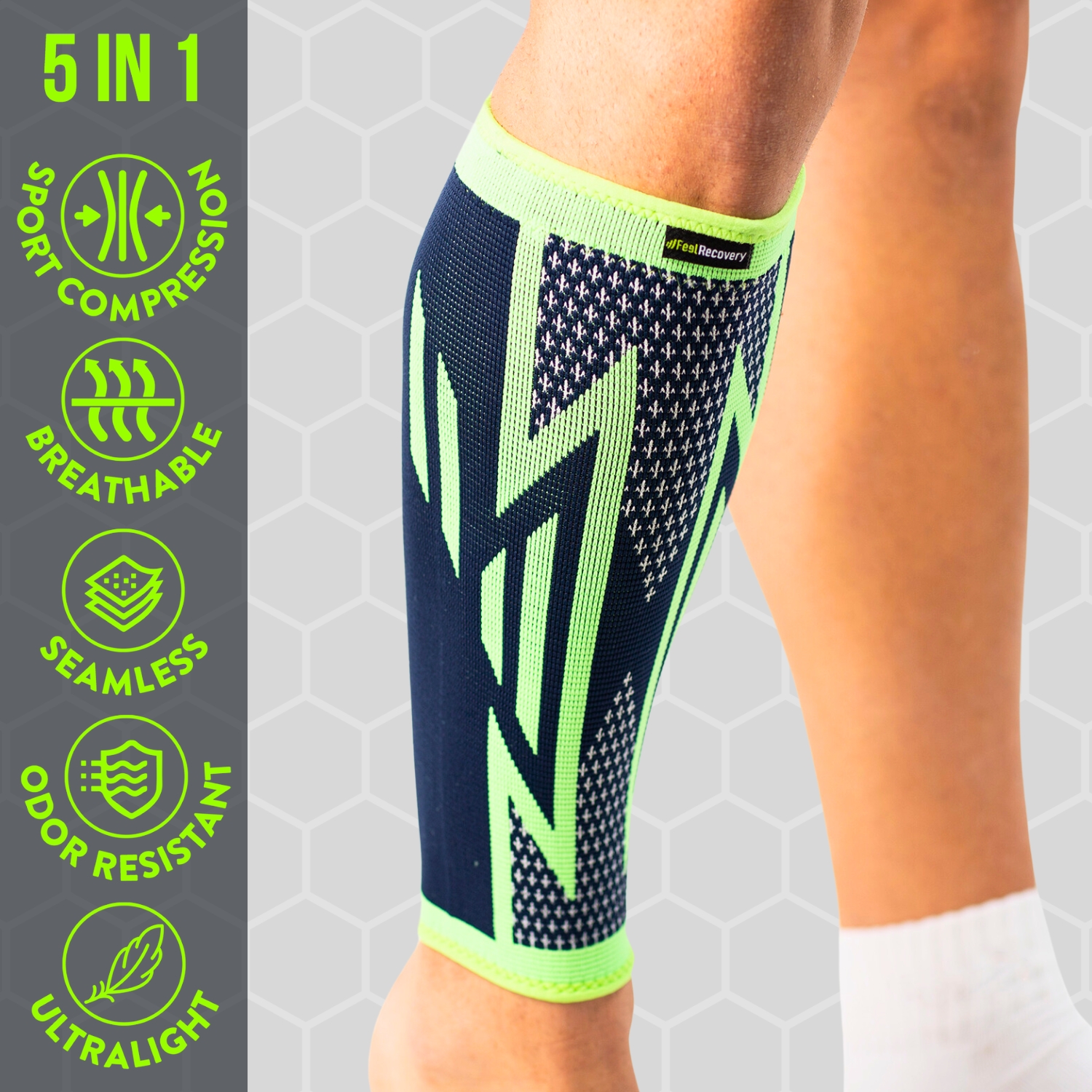
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Green/Navy)
£20,95 -
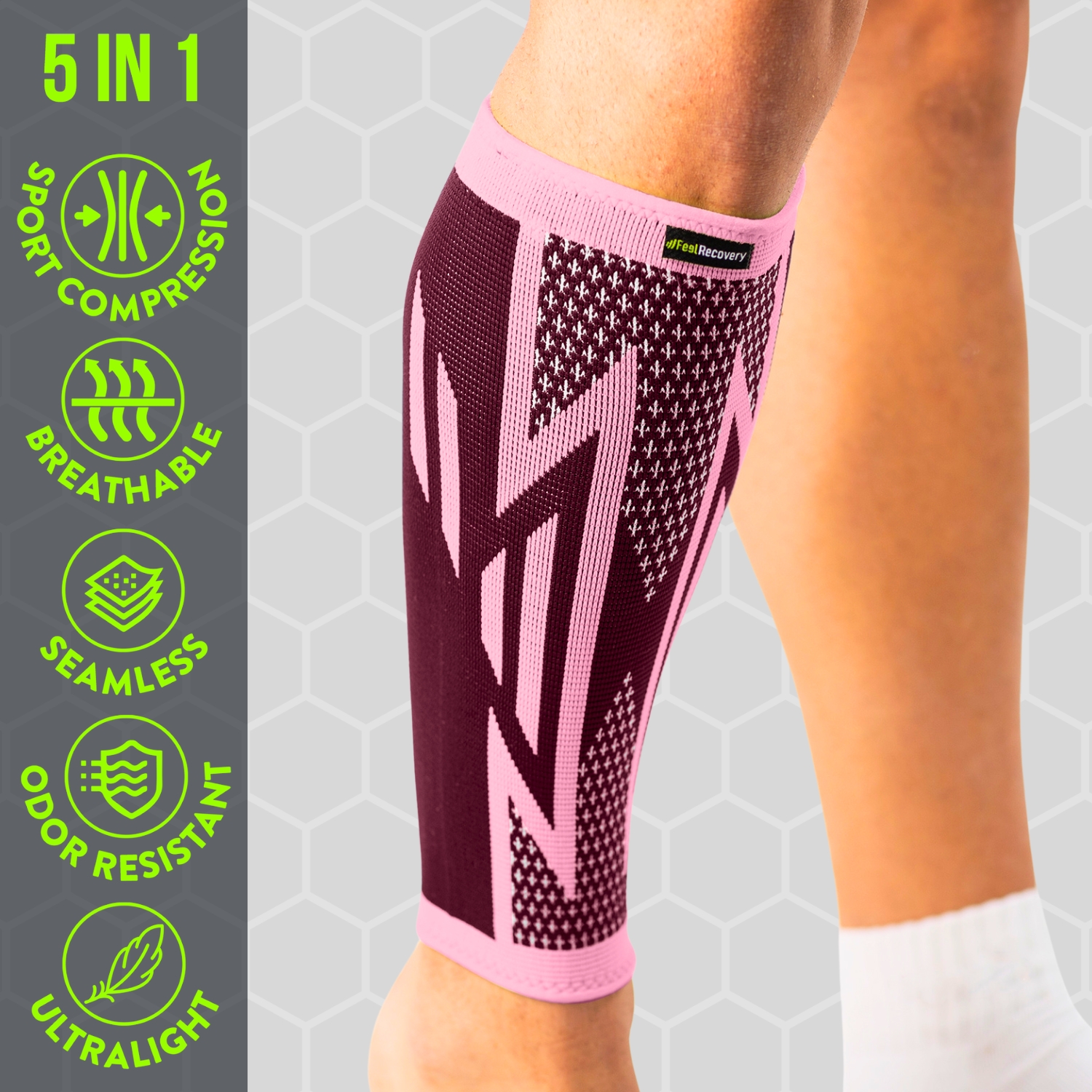
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Pink/Bordeaux)
£20,95 -
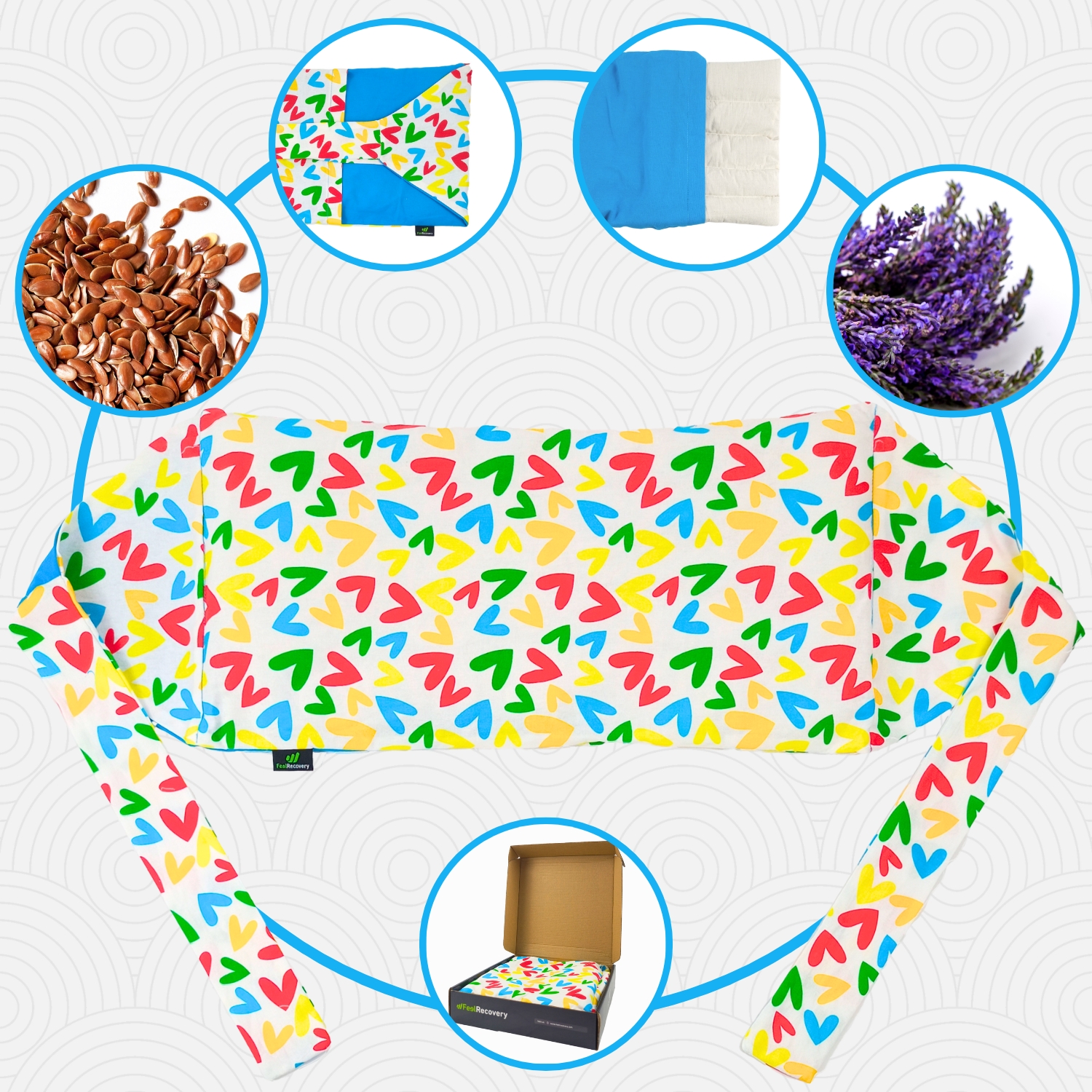
Microwave Wheat Bag for Back Pain Relief (Extra Large) (Hearts)
£24,95 -
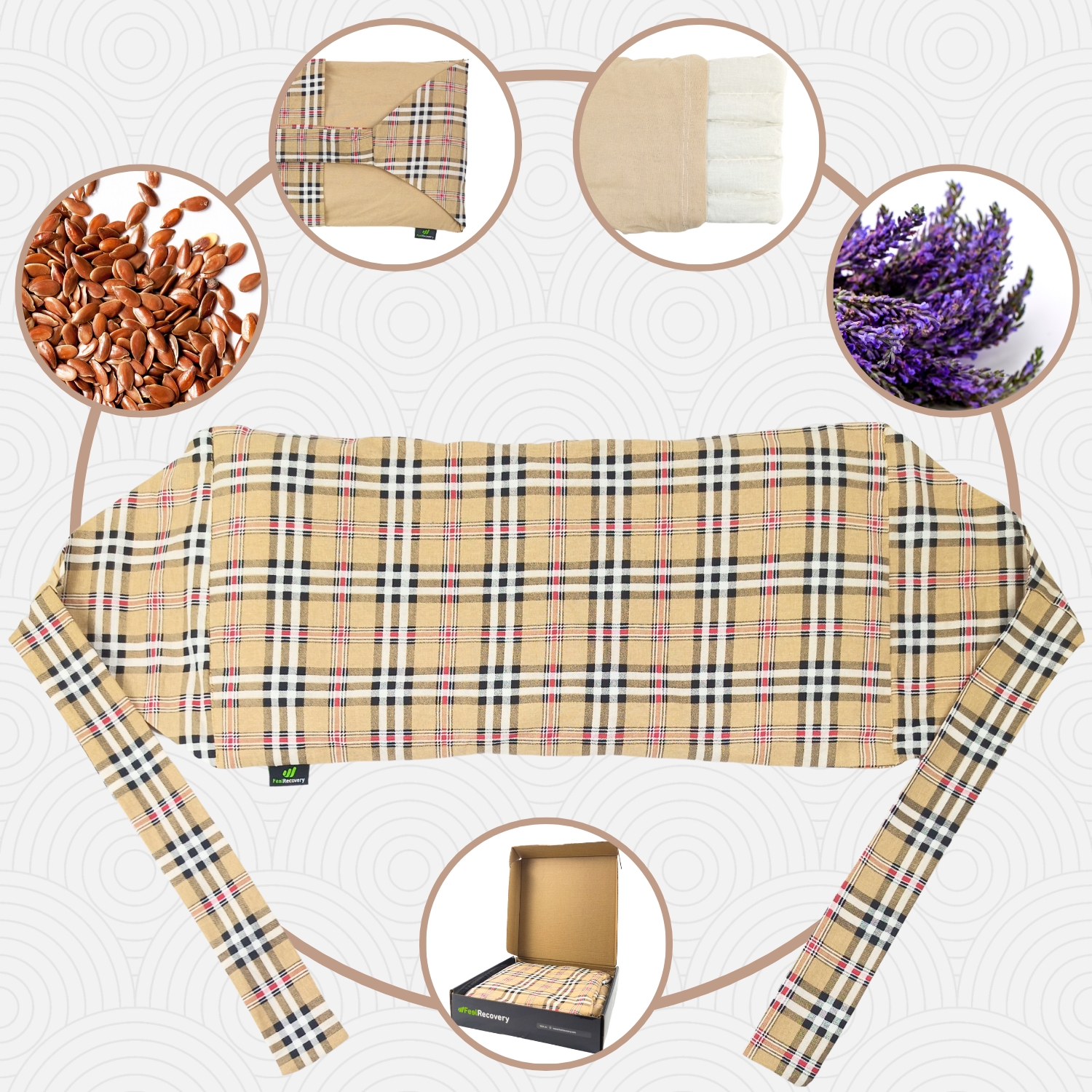
Microwave Wheat Bag for Back Pain Relief (Extra Large) (Oxford)
£24,95 -
Microwave Wheat Bag for Back Pain Relief (Extra Large) (Sport)
£24,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Hearts)
£20,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Oxford)
£20,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Sport)
£20,95 -
Wheat Bag for Microwave Classic Bottle Shaped (Hearts)
£20,95 -
Wheat Bag for Microwave Classic Bottle Shaped (Oxford)
£20,95 -
Wheat Bag for Microwave Classic Bottle Shaped (Sport)
£20,95
-
2 Calf Compression Sleeve (Black/Gray)
£20,95 -
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Black)
£20,95 -
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Green)
£20,95 -
Foot Massage Roller for Plantar Fasciitis (Pink)
£20,95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Black)
£34,95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Green)
£34,95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Pink)
£34,95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Black)
£34,95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Green)
£34,95 -
Soft Density Foam Roller for Recovery (Pink)
£34,95 -
Sport Compression Socks (1 Pair) (Black/Gray)
£20,95 -
Sport Compression Socks (1 Pair) (Green/Navy)
£20,95 -
Sport Compression Socks (1 Pair) (Pink/Bordeaux)
£20,95
Main symptoms associated with calf and leg strains
Pay attention to the following list because we will show you which are the main symptoms that could be related to the appearance of a calf muscle strain:
- Pain when moving the leg: Contracture in the calf and soleus muscles causes intense pain when the person tries to walk or move the lower limb. This is caused by the large amount of metabolites found in the muscle fibres, creating extreme involuntary tension.
- Reduced mobility: The pain may extend to the knees and ankles causing both joints to not work properly. Difficulty walking or jumping is also a common symptom in this type of injury.
- Nodules: In some cases the appearance of lumps in the muscle structure is likely, causing pain to the touch.
- Loss of sensation: Paraesthesia is a common symptom that people suffering from this type of injury have, caused by the lack of dilation of the capillary vessels preventing blood from circulating in a normal way.
- Inflammation: Calf and soleus muscle strain can cause swelling in the area due to the accumulation of residual molecules that cannot be removed by the bloodstream.
How to relieve the pain and improve the symptoms of calf muscle strains?
Calf and leg muscle strains cause pain and inflammation. For this reason, to reduce this symptomatology it is necessary to resort to some of the following treatments.
Alternative and complementary therapies
It is possible to reduce the symptoms of a calf and soleus strain by applying one of the following complementary methods:
- Hot and cold therapy: In order for the cold not to tighten the leg and calf muscles, it is necessary to apply it at a temperature that is not freezing. This will help to obtain all the anti-inflammatory benefits of this type of temperature. By using heat, it is possible to improve the dilation of the vessels located in the area, which allows the soft tissues to deflate and decompress the nerves, thus reducing pain. The practice of this therapy should be directed by a professional and should not exceed 15 to 20 minutes. It must be kept in mind that each temperature must be exposed to the body for no more than 5 minutes, so it is necessary to start with heat.
- Compression therapy: The aim of this treatment is to put constant pressure on the muscular structure in which a strain has occurred in order to stimulate the capillary walls of the tissues. In this way it is possible to increase the blood flow in the leg and calf so that the residual molecules in the fibres can be eliminated by the blood. The use of compression socks will help to reduce pain and swelling and improve the patient's movement.
- Massage therapy: This type of therapy can go hand in hand with the other treatments, as it is considered a non-invasive technique that helps to improve the symptoms of calf muscle strains quickly and effectively. Different techniques can be used to apply heat by floating or tapping the affected area. Care must be taken not to break the walls of the capillaries so that the venules and arterioles can be connected so that the muscles are able to receive the fluids and gases from the blood.
- Acupressure therapy: Pulled muscles in the leg and calf can be treated with this oriental therapy. But it must be taken into account that the aim of this medicine is to seek a mental balance of the patient so that the general tension of the muscular structure decreases. In this way, it helps the person to find harmony to face the pain in the extremities, thus stimulating the nerves located in this sector of the body and the bloodstream.
- Thermotherapy: This is another of the most commonly used treatments in the case of calf muscle contracture. Thermotherapy aims to connect the network of veins and small arteries found in the muscle fibres to each other via capillaries. This allows the blood to work better in removing metabolites or waste molecules from the soft tissue. Therefore, with this type of complementary treatment the symptoms of pain and inflammation are improved.
- Natural remedies using plants: Alternative therapy based on natural plants aims to take advantage of the soothing and anti-inflammatory properties of these herbs. In this way it is possible to reduce inflammation and pain in the calves and calf muscles by means of infusions and baths with warm water. The sessions will depend on the degree of complexity of the injury, which is why it is necessary to consult a doctor so that he or she can approve the use of this treatment. It is possible to find in this therapy the use of citric fruits, ginger, sage and laurel.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: Re-education of the patient is essential to avoid new calf muscle strains. For this reason, the acting doctor should explain to the patient the importance of including different habits in their daily actions that will help their health. In this way, the doctor may address issues related to overexertion, use of appropriate footwear, healthy eating and necessary rest, among other things.
Nutritional supplements
It is possible to reduce the involuntary tension in the calves and calf muscles by taking supplementary nutrients. In this way, vitamins, minerals and proteins are added to the body, although magnesium and potassium are most often found in these powders, syrups or liquids. In addition, this type of therapy brings an extra benefit and that is to avoid the appearance of future injuries in this sector of the body.
Physiotherapy treatments
In calf muscle strain it is possible to reduce the symptoms of pain, swelling and limited mobility. This can be done by means of physiotherapy which uses different procedures to emit heat in the capillary walls.
The result of this complementary treatment is the stimulation of the blood circulation to eliminate the lactic acid located in this part of the body. In this way the metabolites disappear in the exchange of nutrients and oxygen that takes place between the bloodstream and the muscles.
Medications
Opioid analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory drugs are the most commonly used drugs in this drug therapy. Keep in mind that the prescription and administration of this treatment should be directed by the physician.
You should never self-medicate, as this can lead to severe muscular, hepatic and gastrointestinal complications, among other things.
What are the most effective prevention methods for calf and leg muscle pulls?
We will show you below the different factors that you should take into account to avoid calf and leg muscle strain:
- Learn breathing and relaxation techniques: These therapies will help you keep your muscle structure at the right level of tension, causing stress to drop considerably. Meditation is a good resource that you can use to reduce the appearance of calf muscle strains.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Diet and hydration are important components in protecting your leg muscles. This will help you avoid calf strains thanks to the good amount of nutrients in the tissues.
- Avoid the cold: Freezing temperatures tend to cause muscle strains, so you'll need to avoid contact with the cold to lower your chances of calf strain.
- Don't engage in demanding activities: Both sports and jobs where you need to keep your muscle structure at the limit are not recommended. In addition, repetitive and prolonged movements can lead to strains.
- Have correct posture and rest for the necessary time: Tackling daily activities through correct movements will help to avoid muscle strains caused by excessive forces. It is also important to support the leg muscles through adequate rest.
- Keep moving: Engaging in physical activity will help you avoid sedentary muscle fatigue. Keep in mind that this type of action should be done progressively to avoid contractures. On the other hand, don't forget to stretch and warm up your muscles beforehand.
- Incorporate nutritional supplements: After consulting your doctor, you can choose supplements containing B vitamins, minerals and proteins that will help you maintain the correct tension in the muscles of this part of the body.
- Avoid tight shoes and shoes with high heels: These types of shoes place considerable strain on the calf and leg muscles and can cause muscle strain in these muscles.
References
- Green, B., & Pizzari, T. (2017). Calf muscle strain injuries in sport: a systematic review of risk factors for injury. British journal of sports medicine, 51(16), 1189-1194. https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/51/16/1189?hootPostID=8dbac92262359e5c3a3438f4e11668c6
- Bryan Dixon, J. (2009). Gastrocnemius vs. soleus strain: how to differentiate and deal with calf muscle injuries. Current reviews in musculoskeletal medicine, 2(2), 74-77. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12178-009-9045-8
- Hayashi, D., Hamilton, B., Guermazi, A., de Villiers, R., Crema, M. D., & Roemer, F. W. (2012). Traumatic injuries of thigh and calf muscles in athletes: role and clinical relevance of MR imaging and ultrasound. Insights into imaging, 3(6), 591-601. https://insightsimaging.springeropen.com/articles/10.1007/s13244-012-0190-z
- Millar, A. P. (1976). An early stretching routine for calf muscle strains. Medicine and Science in Sports, 8(1), 39-42. https://europepmc.org/article/med/1272005
- Millar, A. P. (1979). Strains of the posterior calf musculature (" tennis leg"). The American journal of sports medicine, 7(3), 172-174. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/036354657900700306
- Orchard, J., & Best, T. M. (2002). The management of muscle strain injuries: an early return versus the risk of recurrence. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, 12(1), 3-5. https://journals.lww.com/cjsportsmed/fulltext/2002/01000/the_management_of_muscle_strain_injuries__an_early.4.aspx
- Noonan, T. J., & Garrett Jr, W. E. (1999). Muscle strain injury: diagnosis and treatment. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 7(4), 262-269. https://journals.lww.com/jaaos/Abstract/1999/07000/Muscle_Strain_Injury__Diagnosis_and_Treatment.6.aspx
- Beiner, J. M., & Jokl, P. (2001). Muscle contusion injuries: current treatment options. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 9(4), 227-237. https://journals.lww.com/jaaos/Abstract/2001/07000/Muscle_Contusion_Injuries__Current_Treatment.2.aspx
- Orchard, J. W., Best, T. M., Mueller-Wohlfahrt, H. W., Hunter, G., Hamilton, B. H., Webborn, N., … & Glasgow, P. (2008). The early management of muscle strains in the elite athlete: best practice in a world with a limited evidence basis. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 42(3), 158-159. https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/42/3/158.short
- Butterfield, T. A. (2010). Eccentric exercise in vivo: strain-induced muscle damage and adaptation in a stable system. Exercise and sport sciences reviews, 38(2), 51-60. https://journals.lww.com/acsm-essr/Fulltext/2010/04000/Stretch_Activated_Ion_Channel_Blockade_Attenuates.00003.aspx