- What is elbow arthritis or inflammation of the elbow joint?
- What are the causes and risk factors for elbow arthritis?
- Best products for elbow arthritis
- Main symptoms that warn us that we have elbow arthritis
- What treatments are available to improve the symptoms of arthritis in the elbow?
- What methods of prevention for arthritis in the elbow are the most effective?
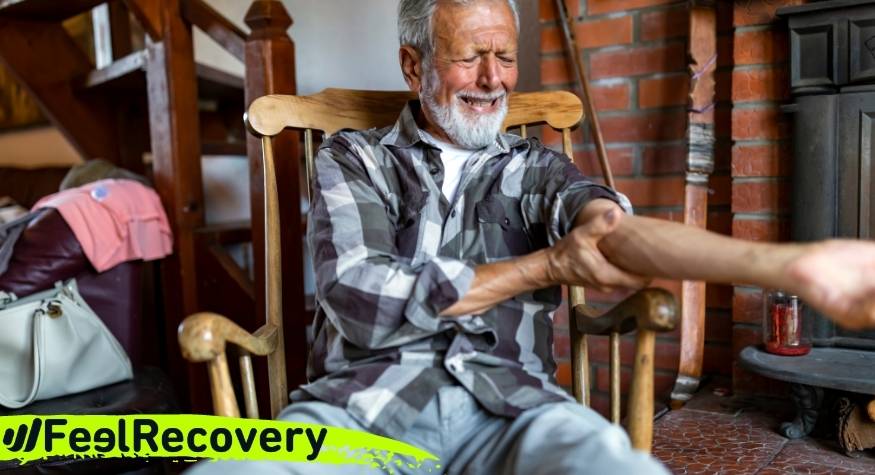
Inflammation in the elbow joint can lead to stiffness in the arm, making it impossible for the patient to carry out everyday tasks normally. For this reason, you should know what elbow arthritis is and what are the causes and risk factors of this pathology. You will find this information in the following paragraphs.
We will also talk about the main symptoms that will warn you about a possible onset of the disease. Finally, you will learn about the current treatments that will help you to improve the symptoms of arthritis and the prevention methods you should keep in mind.
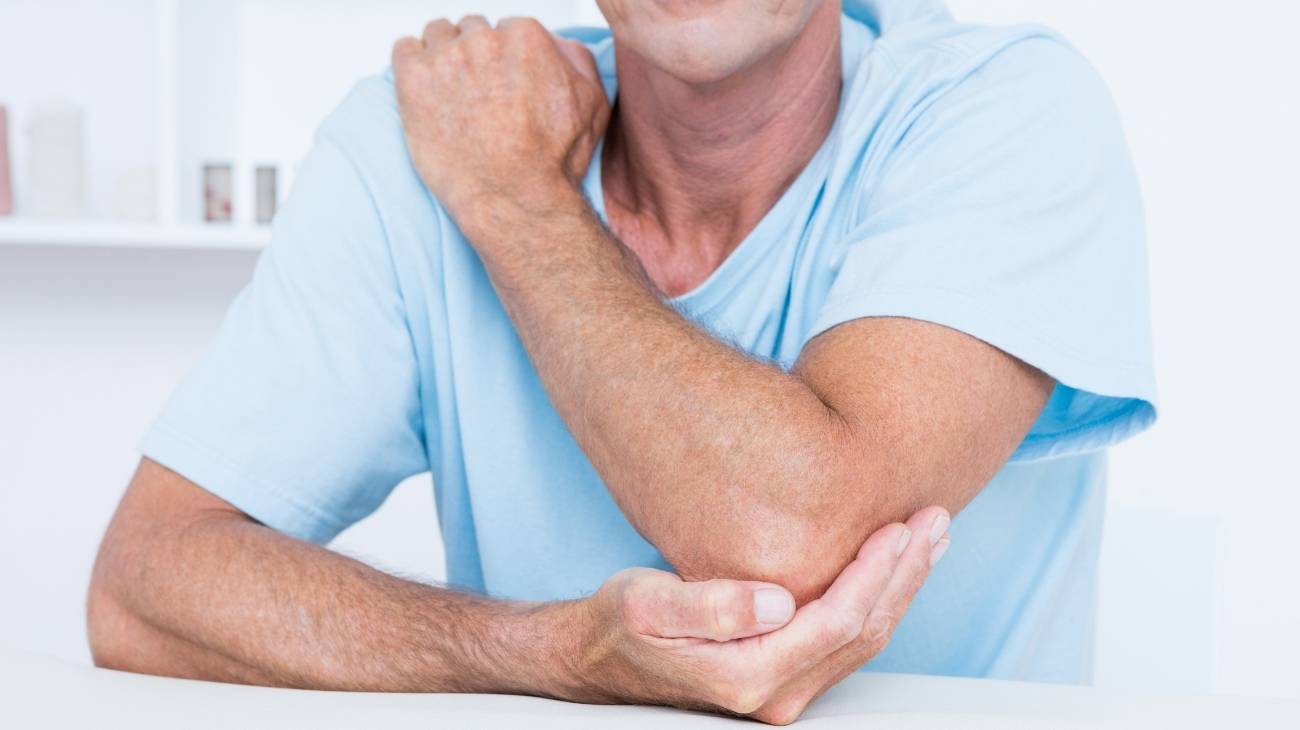
What is elbow arthritis or inflammation of the elbow joint?
Arthritis of the elbow is of the rheumatoid type which occurs in a degenerative manner in the joint and leads, in extreme cases, to the loss of cartilage. The disease is caused by the autoimmune system, i.e. it is caused by an attack of the body's own defence mechanism on the cells of the joint.
The synovial fluid in the elbow is severely affected causing it to thicken and generate an excessive amount of fluid, leading to swelling of the area which, together with the immune system's chemicals, causes pain and stiffness. An important feature of this condition is that the symptoms are most intense after the night's rest period, making it impossible for the patient to bend or straighten the arm.
What are the causes and risk factors for elbow arthritis?
Both the causes and risk factors for elbow arthritis are situations, activities and even genetics that increase the likelihood of contracting the inflammatory pathology. For this reason, it is useful to know which of these risk signs will help you to prevent and detect the disease in advance.
Below is a detailed list:
- Genetics: this is one of the elements that increases the probability of contracting the disease. It is present in both men and women, but according to statistics, elbow arthritis is more common in women, and recent studies have shown that only 5% of patients have parents or siblings with the same condition, so the hereditary factor is no longer considered to be the main cause.
- Trauma to the elbow: If the person performs an activity that exhaustively exposes the work of the joint, causing injuries, it is likely to generate rheumatoid arthritis in the elbow in the future. In this case, it is advisable to consult a doctor periodically to find out if there is significant wear and tear on the joint.
- Presence of bacteria, fungi or viruses: these can be caused by trauma to the elbow as a result of the activity carried out. These pathogenic bodies travel through the blood and settle inside the joint cavity with synovial fluid, which can lead to septic arthritis.
- Physical defect of the articular cartilage: this is located within the synovial membrane. It is possible to develop arthritis if this component has natural developmental defects. To counteract this cause, it is important to monitor the joint with X-rays and other clinical studies.
- Lack of appropriate response from the autoimmune system: It should not be forgotten that arthritis is autoimmune, meaning that it is the body's own protective structure that attacks its own cells, causing severe complications within the synovial membrane. For this reason, the immune system is also considered a risk factor.
- Overweight: Weight is one of the most important causes of arthritis. You must be very careful because the wear and tear on the joints caused by being overweight is very common, leading to the onset of arthritis.
Best products for elbow arthritis
Bestseller
Main symptoms that warn us that we have elbow arthritis
Symptoms to look out for that may help you to notice that you have arthritis in your elbow are as follows:
- Swelling in the joint area: In some cases it is accompanied by a redness that is warmer to the touch than the area that does not surround it.
- Numbness or a tingling sensation: in the elbow are symptoms to be taken into account and a doctor should be consulted immediately.
- Reduced flexion and extension: If bending or extending the arm becomes difficult after sleep, causing stiffness in the joint area, it is likely to be a cause of arthritis.
- Joint deformity: Arthritis causes the bone to thicken and outgrow the synovial membrane, resulting in significant deformity to the naked eye.
- Intestinal symptoms: If you have nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite or weakness for no reason and you also have any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should urgently consult a rheumatologist about possible arthritis in the elbow.
- Lumps: Appearance of a hard, and in some cases rough, lump on the outside of the joint. This epidermoid lump can be as large as a walnut and is easy to detect by touch.
- Existence of a rheumatoid nodule located under the skin: This lump does not cause pain and is generally small in size. To be sure of this pathology, it is necessary to carry out X-ray studies.
- Reduced mobility: In advanced stages of arthritis in the elbow, the patient may be unable to turn the palms of the hand.
- Increased fatigue: A cause related to arthritis that few people give importance to is permanent fatigue for no apparent reason.
What treatments are available to improve the symptoms of arthritis in the elbow?
There are different treatments that can be applied to improve the symptoms of elbow arthritis, but you must bear in mind that they must be supervised by a rheumatologist. And if you are considering alternative therapy, you should consult with your rheumatologist before starting.
See how to treat rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow:
Alternative and complementary therapies
Alternative therapies are treatments that are developed holistically and are tailored to the individual patient. In this way, it is possible to include different methods as a complement to conventional therapy, which is based on medication.
We will show you below what these alternative therapies are and why you should use them in the treatment of arthritis of the elbow, always under the supervision of your doctor:
- Heat and cold therapy: when heat and cold therapy is used, the aim is to temporarily reduce the pain of elbow arthritis and reduce muscle spasm for better flexion and extension. Ice packs and hot water packs are used for this purpose. It is important to keep in mind that patients respond differently to this treatment, so it is necessary to consult a doctor about the ideal temperature for each person. For the therapy to be effective, the session should never exceed 20 minutes and a cloth should be placed between the skin and the element that will emit the temperature to avoid ulcers in the epidermis.
- Compression therapy: although it is not a technique widely used in elbow arthritis, compresses can be used to prevent movement of the arm and thus correct deviations of the bone or articular cartilage. With this therapy it is also possible to soften the joint so that the patient does not feel pain and thus reduce muscle tension. This treatment must be prescribed by a doctor.
- Massage therapy: Massage is a good alternative that can be used to relax the patient and prevent mental and physical stress attacks. The technique used in massage therapy should be carried out by a qualified person to avoid further injury. The patient himself can also rub the elbow area gently to stimulate the musculature, but it should not be forgotten that before choosing this treatment a doctor should be consulted.
- Acupressure therapy: Transcutaneous nerve stimulation aims to inhibit pain by preventing electrical signals from reaching the brain so that the patient feels less discomfort in the affected area and therefore suffers less. Thanks to the stimulation of endorphin release, which works as an analgesic, it is possible to avoid and reduce the sensation of numbness in the elbow. Acupressure consists of pressing the palms of the hands, feet and other areas of the patient's body to produce a feeling of well-being generated by the stimulation of the tissues and the nervous system. In this Chinese medicine, only the therapist's hands are used.
- Thermotherapy: this rehabilitative approach consists of promoting moist heat at different temperatures. This therapy is based on stimulating heat in the affected area by means of hot water bags to reduce the spasm and thus obtain a better flexion-extension of the elbow, increasing the patient's quality of life.
- Natural remedies using plants: Medicinal herbs are plants that are used as a complement to pharmacological treatment to prevent pain, reduce muscle tension and reduce inflammation in the area affected by arthritis. But in no case does it replace traditional therapy, so you should consult your doctor if it is advisable to use natural remedies with the use of plants. Among the most common herbs that you can find in these types of treatments are mint, lavender, ginger, chamomile and green tea, among others. Their mode of application differs according to the plant chosen.
- Ultrasound: by means of a frequency that exceeds 20,000 vibrations in one second, it is possible to reduce muscle spasms, improve the flexion and extension of the arm and eliminate discomfort in the joint. For this it is necessary that the technique is carried out by a professional therapist and that the rheumatologist is consulted beforehand to find out if this complementary therapy will help the patient's current situation.
- Meditation and relaxation: the aim of this complementary psychological medicine is to lower the patient's stress by means of muscle-relaxing thoughts and thus create a calm mind. Its practice needs to be guided by professionals who are skilled in the field. Breathing techniques are the key to the patient perceiving and responding to the illness from a completely different and positive point of view.
- Aromatherapy: to improve the patient's well-being, whether physical or psychological, different aromatic elements are used to complement traditional therapy. Both essential oils and other aromatic combinations can be used in different ways to bring about relaxation, relief and revitalisation of the patient. Vanilla, eucalyptus, cinnamon, citrus fruits, jasmine and mint are some of the aromatic components used in this alternative therapy. Its use is simple, just rub a handkerchief moistened with these essences over the face and hands until a feeling of calmness is provoked. It can also be used by means of candles and infusions.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine is used to reduce heaviness and discomfort in the elbow through the Shu points. This treatment is carried out using several hot needles, or moxibustion, which are placed in strategic places in the affected area following a certain pattern. The aim of this therapy is to provoke an almost immediate feeling of satisfaction in the patient.
- Biofeedback: this complementary technique consists of letting the patient know how their body reacts each time their muscles tense and they feel pain in their elbow joints. It is necessary to use electronic equipment to measure different parameters in each situation of stress caused by the disease. It is ideal to use this treatment with meditation therapy to show the contrast that the body generates in a relaxed situation. This will help the patient to better control the pain.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: Battling pain is one of the most traumatic consequences of elbow arthritis. For this reason, it is advisable to teach the patient what causes the pain, why it originates and how to deal with it by improving different aspects of daily life.
Dietary supplements
Dietary supplements are pills or syrups that are included in this alternative therapy and are based on substances and chemical compounds that alleviate the symptoms of elbow arthritis. They are products that supplement the patient's diet during conventional treatment. For their use it is necessary to know the scientific evidence supporting the results in order to avoid side effects; therefore, it is necessary to consult a rheumatologist before opting for this therapy.
Physiotherapy treatments
Physiotherapy is concerned with strengthening the elbow through exercises that are applied precisely to the joint. This helps to improve the patient's flexibility, mood and sense of well-being. It is necessary to consult a doctor before practising this technique and it is important to remember that it must be carried out by a professional physiotherapist to avoid serious injury. It can be carried out with special equipment and even under water.
Medicines
You should bear in mind that the medicines used must be prescribed by your doctor, so you should never self-medicate. Among the most commonly used drugs as a basis for treatment are painkillers and non-steroidal inflammatory agents. But these drugs are generally used for a short time, as the side effects are notorious in controlling rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow.
Accordingly, anti-rheumatic drugs, known as DMARDs, are used. Corticosteroid-type drugs are also used to combat elbow arthritis to act as anti-inflammatory drugs. Biological agents are also prescribed in the treatment of elbow arthritis, and monoclonal agents can be found in this therapy. These include Rituximab, Etanercept, Infliximab, Tocilizumab and Abatacept.
Surgery
Surgical interventions are recommended when the disease is advanced and drug treatment is not sufficient. This avoids lesions that may become more serious in the future. Depending on the location of the joint, elbow arthritis is treated by removing the membrane containing the synovial fluid by means of a synovectomy. However, it is also common to see an arthroplasty to place a prosthesis to replace the function of the elbow.
What methods of prevention for arthritis in the elbow are the most effective?
To avoid elbow arthritis it is important to take into account the following methods:
- Don't do sudden activities that put your elbow at risk: It is necessary to protect your joints if you have to exert yourself on a daily basis, for this reason you must learn to lift heavy objects and position your arms correctly to avoid injuries that can lead to arthritis.
- Don't play high-impact sports: these can increase the likelihood of muscle spasms, strains and other serious injuries. If you do this type of activity, it is necessary to warm up all joints, especially the elbow, beforehand.
- Eat a balanced diet: Foods low in sugar will help to reduce the likelihood of arthritis. In addition, you should accompany your meals with vegetables rich in vitamin D, olive oil, nuts and fish with the highest amount of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Be physically active on a daily basis: No matter how old you are, it is important to walk 30 minutes a day, ride a bike or do any other cardiovascular activity. This will help prevent arthritis by strengthening your body and reducing the risk of joint cartilage wear and tear.
- Control your weight: While weight gain is a consequence of sports and a balanced diet, it is important to keep in mind that obesity is a major factor in elbow arthritis.
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco: To avoid osteoporosis you should eliminate the intake of drinks, drugs and tobacco.
- See your doctor regularly: Especially if you are a woman going through menopause. This will help you know how to balance the lack of oestrogen and keep calcium in your body. Also, for both men and women, if you feel any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should be alert and consult a health professional as a matter of urgency.
References
- Soojian, M. G., & Kwon, Y. W. (2007). Elbow arthritis. Bulletin of the NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases, 65(1). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17539763/
- Kokkalis, Z. T., Schmidt, C. C., & Sotereanos, D. G. (2009). Elbow arthritis: current concepts. The Journal of hand surgery, 34(4), 761-768. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0363502309001610
- Morrey, B. F., & Adams, R. A. (1992). Semiconstrained arthroplasty for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow. JBJS, 74(4), 479-490. https://journals.lww.com/jbjsjournal/Abstract/1992/74040/Semiconstrained_arthroplasty_for_the_treatment_of.3.aspx
- Morrey, B. F. (1992). Primary degenerative arthritis of the elbow. Treatment by ulnohumeral arthroplasty. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British volume, 74(3), 409-413. https://online.boneandjoint.org.uk/doi/abs/10.1302/0301-620x.74b3.1587890
- O'Driscoll, S. W. (1995). Operative treatment of elbow arthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 7(2), 103-106. https://journals.lww.com/co-rheumatology/abstract/1995/03000/operative_treatment_of_elbow_arthritis.6.aspx
- Sibley, J. T. (1985). Weather and arthritis symptoms. The Journal of Rheumatology, 12(4), 707-710. https://europepmc.org/article/med/4057192
- SCHAIBLE, H. G., Ebersberger, A., & Von Banchet, G. S. (2002). Mechanisms of pain in arthritis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 966(1), 343-354. https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04234.x
- Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D., Koeller, M., Weisman, M. H., & Emery, P. (2007). New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. The lancet, 370(9602), 1861-1874. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140673607607843
- Burmester, G. R., & Pope, J. E. (2017). Novel treatment strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. The Lancet, 389(10086), 2338-2348. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140673617314915
- Majithia, V., & Geraci, S. A. (2007). Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis and management. The American journal of medicine, 120(11), 936-939. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002934307003610