For those with arthritis and osteoarthritis, finding a quick, simple and economical solution is very important. When pharmacological solutions are not available the easiest solution is to use gel packs for hot and cold.
Therefore, it is necessary to know how to use hot and cold gel packs to relieve the pain of arthritis and osteoarthritis. These two joint pathologies are very different in their origin, but both cause inflammation and pain. Take a look at what follows and learn about their benefits. Let's go!
What are the causes and origin of arthritis and osteoarthritis pain?
As we have already mentioned, arthritis and osteoarthritis are two very frequent pathologies of the joints. Even so, they have totally different origins and causes, which is why their treatment tends to vary. We can define them in this way:
Arthritis
Arthritis is defined as an inflammation and deterioration of one or more joints and can have more than 100 causes. The structures that can be affected involve cartilage, synovial fluid, the bones that make it up, ligaments, tendons or bursa.
This disease is commonly due to autoimmune inflammatory diseases, uric acid or calcium pyrophosphate crystals and infection by viruses or bacteria. It can occur in any sex and at any age, and the pain it causes can be disabling.
Among the most common causes are:
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: This is an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic joint pain and inflammation in childhood and youth. Its cause is completely unknown but it is believed that the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissues such as joints. It can cause severe joint pain and inflammation and is accompanied by fever and other symptoms.
- Adult rheumatoid arthritis: This disease has the same presentation as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and is also autoimmune. However, the age group is over 16, and it is much more common in women. Also, it causes severe and chronic inflammation and pain in the joints.
- Gouty or crystal arthritis: In this case, inflammation of the joints occurs due to the accumulation of uric acid or calcium pyrophosphate crystals. This is because the body does not produce much uric acid or is not able to get rid of it. It is a very painful and recurrent condition and several joints may be involved.
- Viral and bacterial infections: Some viral infections can be associated with inflammation of the joints. Injuries or infections to the skin adjacent to a joint can encourage the penetration of bacteria and cause arthritis. This type of arthritis is called septic arthritis and is a rather delicate condition.
- Other diseases: Diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma and psoriasis can lead to arthritis. Although these pathologies are not exclusive to the joints, they are autoimmune and the body may react against them at some point.
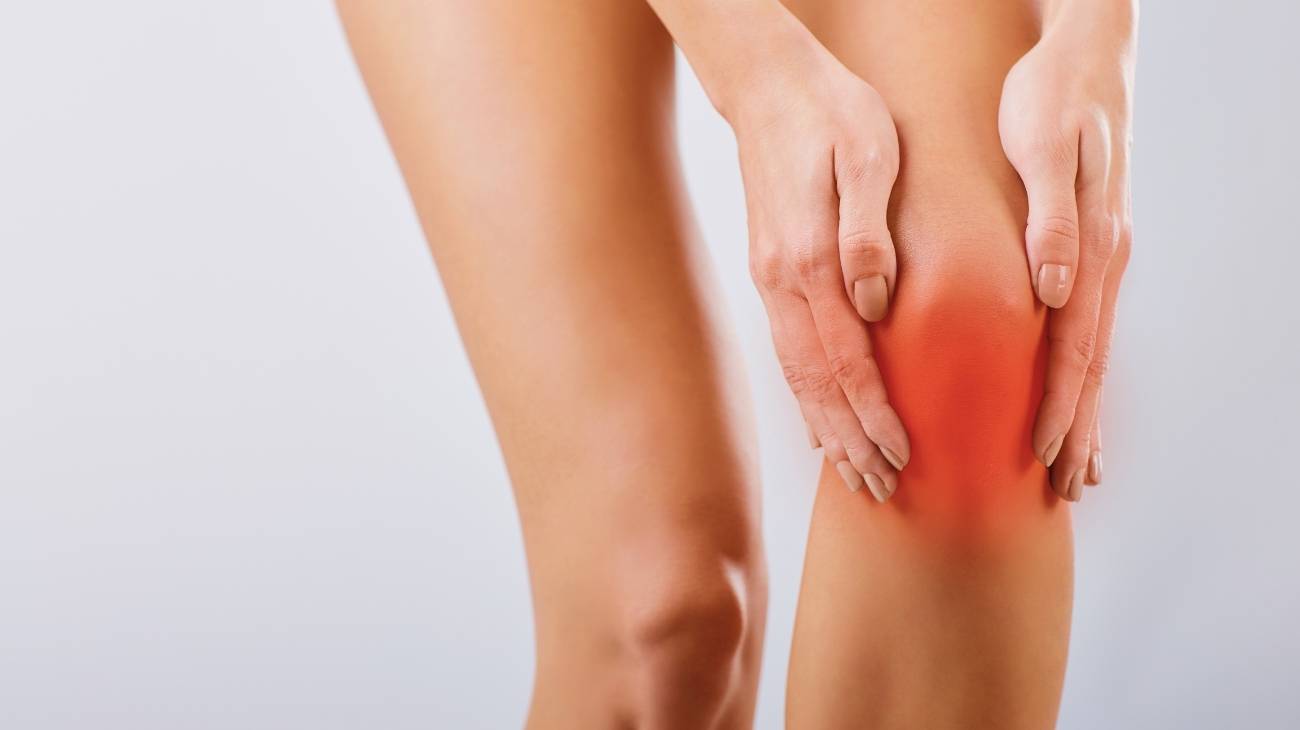
Osteoarthritis
This type of joint inflammation has a completely different origin than arthritis. In this case there is a wearing out, breaking down and ageing of the joint cartilage in one or more joints. It is much more frequent in the hip, knee and foot joints, but can appear in other joints.
Osteoarthritis usually occurs after the age of 40 and can affect both men and women. When there is this wear and tear, it causes a lot of pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected limb. As the years go by there is more deformity of the joints and more stiffness and weakness in ligaments and tendons.
The most frequent causes of osteoarthritis are:
- Old fractures: Fractures in the joints involve a process of repairing the bone, leaving an overgrowth of bone. This type of injury can lead to damage to the cartilage and adjacent ligaments. They usually affect more over the years.
- Overweight: Excessive body weight can cause breakdown and wear of articular cartilage in supporting joints of the body. It most commonly affects the hip, knee, ankle and foot joints. It generates a lot of pain and swelling and the mobility of the affected joint is compromised.
- Some jobs or daily activities: The repeated movement in a joint can generate wear and tear of the articular cartilage. Activities that involve daily kneeling, squatting, climbing stairs, walking, and lifting can all be affected.
- High-impact sports: Practicing sports that have a greater impact on the joints generates osteoarthritis. Among the sports that can affect you is football because it generates a direct impact on the joint. Also, basketball and baseball by twisting or throwing repeatedly.
Bestseller
What is best for reducing joint pain from osteoarthritis, cold or heat?
Heat and cold are very good for relieving joint pain from arthritis and osteoarthritis if you know when to use them. You cannot conclude that one is better than the other, because both bring great benefits for the ailments.
Below, we'll tell you about the benefits of each:
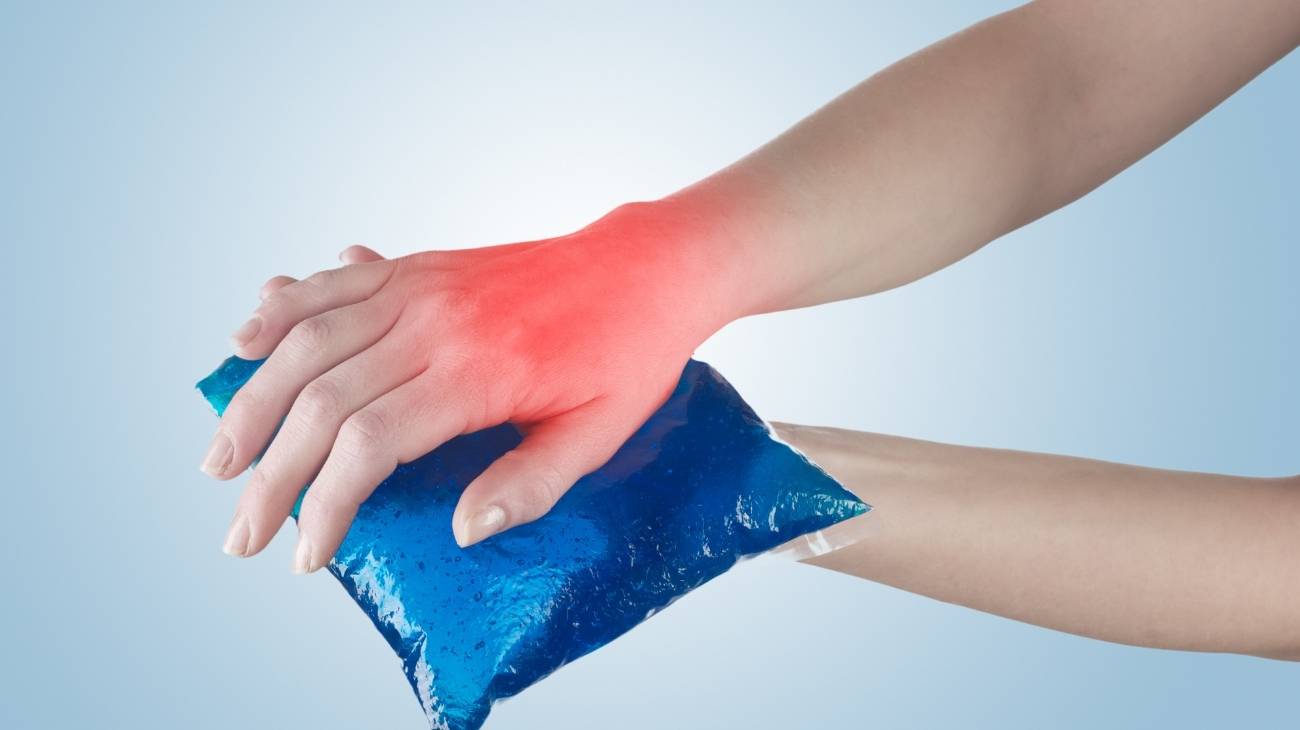
Benefits of applying cold
Cryotherapy is one of the best solutions for joint pain and inflammation. It is very useful in the acute inflammatory phase of arthritis where there is a lot of pain and inflammation. But, it can also be used in osteoarthritis when the wear and tear on the cartilage causes further inflammation of the tendons and ligaments.
It is a very effective and easy to perform solution so pay attention to these great benefits:
- It reduces inflammation: The first faculty that cold has when it is placed in any part of the body is the vasoconstriction in the tissues. This causes a considerable reduction of the blood flow to reduce the edema and inflammation. Used in acute inflammatory processes it is very effective and prevents inflammation from becoming complicated.
- Calms pain: The cold works as a powerful analgesic. When you put cold on an area you will feel initially cold, then a mild burning, then pain and finally numbness. In this way, the pain is relieved and with its anti-inflammatory properties it improves the condition considerably.
- Less tissue damage: The limited blood flow prevents the precursors of inflammation from damaging adjacent tissues. Therefore, cryotherapy is an excellent option in the acute phase of arthritis where the body reacts to itself.
Benefits of applying heat
Heat also has potential benefits for joint pain. Being a powerful vasodilator it cannot be placed in inflammatory processes. However, it is very good for improving the elasticity and flexibility of the tendons and ligaments in the joints.
Thermotherapy is also one of the easiest therapies to perform:
- Controls muscle spasms: The muscles involved in the affected joint can spasm and therefore generate pain. Heat generates a better blood flow which considerably reduces spasms and chronic pain. It is most useful in pathologies such as osteoarthritis.
- It restores elasticity and flexibility: The heat causes a better relaxation of the ligaments and tendons. The vasodilation caused by the heat improves blood flow and this allows for better mobility of the affected joint.
- Greater recovery of damaged tissues: As there is greater blood flow in the affected area there will be a better distribution of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues. This allows tissues such as ligaments, tendons, muscles and even the articular cartilage itself to have a chance to regenerate.
How can hot/cold gel packs be used to reduce inflammation from arthritis in the joints?
The cold/hot gel packs are very easy to use, as they do not involve any major effort or complicated processes. Pay attention to these simple recommendations for the correct use of this product:
Ice gel packs
The process for cooling the gel packs is quite simple:
- Put them in the freezer or refrigerator to cool for 60 minutes. This time represents the minimum time for them to generate the desired effect.
- After that time, take them out of the freezer and start placing them on the affected joint. If you feel it is too cold you can wait a few minutes and then start using.
- Give the affected joint a 10-15 minute exposure time with a 1 hour rest time.
- You can use them for a period of 48-72 hours to achieve a reduction in swelling in the joint. After the improvement of the inflammation it is recommended to continue its use to improve the relaxation of the adjacent tissues.
- Always avoid placing them directly on the skin as the cold can cause irritation and burns. Use a cloth or cover to place them, although our gel packs do not require their use. They can be used directly because they all have a soft protective layer on one side.
- When the exposure time in the affected joint is over, return the ice gel pad to the freezer.
Hot gel packs
Heating a gel pack is very simple, however, our gel packs are not designed to be heated. Therefore, if you need to use them in heat, it is best to use an 800W microwave oven or a bain-marie. Follow our recommendations to the letter:
- If you are going to use a microwave oven, place the pad at 800 W for 20-30 seconds (depending on size). It is necessary to supervise the temperature and check that it is warm to the touch. It is important to massage the gel so that the heat is distributed evenly.
- If using a water bath, bring the water to a boil. When it has boiled, remove the pot from the kitchen and insert the pack. After 7 to 8 minutes it will be ready to use, so take it out and dry it well with a cloth.
- Place it on a dry cloth or cover and place it on the affected joint for 10 to 20 minutes with 1 hour's rest. You can repeat the exposure time several times a day for as long as necessary.
- It is important not to exceed the temperature because it can cause damage to the structure of the pouch and break it. If this happens, wait for it to cool down to room temperature and discard it immediately.
- Do not in any way attempt to heat a frozen gel pack. Always wait until it is at room temperature before starting the heating process.
- Never try to heat a gel pack in an oven, it can be very dangerous and you will end up damaging the product.
- If you need to use them again after the exposure time, wait for them to cool down before reheating.