- What are abdominal cramps due to gas cramps?
- What are the causes of abdominal pain due to gas colic?
- Best products for Stomach cramps
- Main symptoms associated with abdominal cramps due to gas colic
- How to relieve abdominal pain due to gas colic?
- What are the most effective prevention methods for abdominal cramps due to gas colic?
Suddenly, many people are affected by a strong contraction in some part of their body that tightens up and makes it difficult to move or function normally. This is basically known as "involuntary cramps" and can harm any patient regardless of age.
However, one of the most common spasms are those that occur in the abdominal area due to the accumulation of gases that produce acute colic. It is therefore of great interest to know what abdominal cramps specifically are, as well as their causes, symptoms, treatments and methods of care.
What are abdominal cramps due to gas cramps?
While it is true, a cramp is a contracture that produces a noticeable pain temporarily and prevents relaxation of the area in which it occurs. Thus, abdominal spasms are defined as uncontrollable muscle movements in the abdominal area that translate into cramps in the stomach and cause discomfort between the chest and groin, known as the "abdominal region".
Generally, this type of cramps are caused by the presence or accumulation of gases that tend to produce strong cramps that trigger the painful spasms in that area. As a result, it is a condition that disturbs both children from the age of 5 years and adults (more often women).
What are the causes of abdominal pain due to gas colic?
In many cases, women suffering from gas cramps tend to confuse them with menstrual cramps, as they originate in the belly area. For this reason, it is essential to know what are the main motives, factors or reasons that trigger these spasms and/or increase the risk of experiencing one of them, in order to be able to act correctly in the face of this discomfort.
The following are the causes of abdominal pain due to gas colic:
- Constipation or difficulty passing stools for a certain period of time.
- Food poisoning that is caused by food contaminated with toxins, parasites, bacteria or viruses.
- Dyspepsia or indigestion caused by drugs or a gastroduodenal ulcer.
- Allergy to certain drugs that causes the immune system to react abnormally.
- Lactose intolerance which is defined as the inability to digest dairy sugar completely.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) which causes changes in the intestine and usually follows a bacterial or parasitic intestinal infection.
- Another cause of these spasms is cancer of the stomach, large intestine (or colon) and other associated organs, but these causes are in the minority.
- Intestinal ischaemia, which reduces the blood supply to the intestines, also causes abdominal cramps.
- If gastro-oesophageal reflux or heartburn occurs, the patient may suffer from contractures in the stomach area.
- Pregnancy also alters the functioning of the stomach and causes muscle spasms that are painful (but not usually of a serious nature).
Best products for Stomach cramps
Bestseller
-
Microwave Wheat Bag for Back Pain Relief (Extra Large) (Hearts)
£24,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Hearts)
£20,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Oxford)
£20,95 -
Microwaveable Wheat Bag for Pain Relief (Sport)
£20,95 -
Wheat Bag for Microwave Classic Bottle Shaped (Hearts)
£20,95 -
Wheat Bag for Microwave Classic Bottle Shaped (Oxford)
£20,95 -
Wheat Bag for Microwave Classic Bottle Shaped (Sport)
£20,95
Main symptoms associated with abdominal cramps due to gas colic
Once spasms arise in the abdominal area of the body, certain signs and symptoms automatically appear that are characteristic of this condition triggered by colic due to the accumulation of gas. These alter the regular functioning of the body, especially in the stomach region from the chest to the groin.
It is important to know which are the signs that describe the pathological state caused by contractions in the abdomen and here, we point out the most common ones:
- Severe pain in the abdominal part of the patient.
- Inflammation or swelling in the abdomen and even in the legs.
- Frequent diarrhoea and/or vomiting.
- Great difficulty in swallowing or swallowing.
- Fever or increase in average body temperature.
- Occasionally, there is blood in the stool, vomit or urine.
- Rash and yellowing of the skin and even the whites of the eyes (jaundice).
How to relieve abdominal pain due to gas colic?
Fortunately, there are different therapies and treatments that help to attenuate the pain and discomfort generated by spasms in the abdomen due to colic and gas. These are basically alternative and natural therapies, as well as dietary supplements and certain medications indicated to treat this condition.
Here are the best approved techniques for relieving abdominal pain due to sudden abdominal cramps:
Alternative and complementary therapies
One of the most recommended solutions to soothe the symptoms of stomach cramps are complementary therapies, which naturally tend to channel a healing response in the body to minimise the individual's pain.
In this case, the most recommended of all are the following:
- Massage therapy: Therapeutic massages are effective in treating spasms in the stomach area. When the specialist rubs the affected area with the appropriate techniques, this will help to increase blood flow to reduce discomfort and even reduce inflammation.
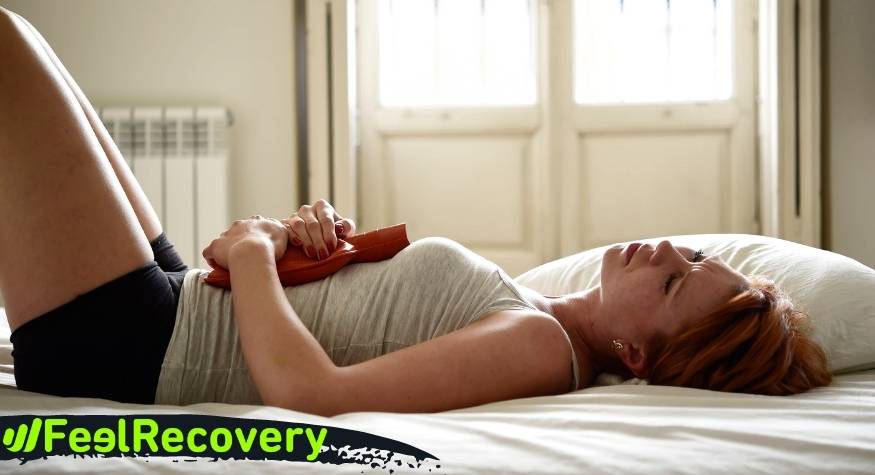
- Thermotherapy: By default, thermotherapy uses heat to provide an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and relaxing effect on any area of the body that has been contracted. As it improves blood circulation and decreases the pain patients experience from cramps. Therefore, it is recommended to apply thermotherapy or above body temperature to the abdomen to relieve the ailment, either with gaseous, semi-liquid or solid heat.
- Natural remedies using plants: Without a doubt, natural remedies are also excellent allies to treat pain caused by spasms in the stomach. Several plants promote the improvement of blood circulation, are ideal for deflating the abdomen and also help to soothe the pain. In this case, you can resort to: drinking ginger tea or adding this remedy to food, drinking peppermint tea or juice, applying an arnica infusion to the area, adding cinnamon to the food you want, eating basil, consuming peppermint, drinking coconut water and swallowing bananas or plantains.
- Meditation and relaxation: Another way to attack the intense ailment is by practising relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation. This helps the body to release any tension, which, as a result, eliminates the present discomfort and thus attenuates the pain generated by spasms in the abdominal region. For this, in addition to yoga and meditation, you can also do tai chi, music therapy and deep breathing.
- Aromatherapy: Through essential oils or aromatic liquids from flowers, plants, herbs and bark, aromatherapy is a treatment that offers excellent analgesic effects to eliminate pain in the human body and also manages to relax muscles, avoid anxiety and boost defences to prevent contractures in any part of the body. In this case, you can implement this therapy with aromas such as: lavender, camphor, basil, tangerine, walnut, parsley and oregano.
- Acupuncture: This is a key component of traditional Chinese medicine that is recommended to lessen the symptoms of cramps in any muscle in the body and is therefore ideal for treating stomach spasms. It is based on the insertion of fine needles in certain strategic parts of the body, applying the corresponding pressure and massaging the recommended acupuncture points, which guarantees the reduction of pain in the abdominal area.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: If patients adopt healthy habits in their daily lives, they will be able to stop suffering from stomach spasms and even prevent them for life. These habits lead to the proper functioning of the body in general and thus, the body is able to hinder the onset of cramps. To achieve this, you can do the following: prevent anxiety and stress with relaxation methods, consume plenty of water to prevent the accumulation of gas, eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals, exercise gradually, bring forward the time of dinner and control the amounts of food you eat.
Dietary supplements
If people who suffer from cramps in the abdomen due to gas cramps start to eat a healthy diet combined with certain food supplements, they will be able to alleviate the symptoms caused by these contractures and will also be able to avoid this ailment in the future.
These supplements will improve the well-being of the organism by providing it with good quantities of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, fatty acids and enzymes.
Therefore, in order to avoid the deficiency of certain minerals or vitamins that tend to trigger spasms in the body, sufferers should consume some food supplements to balance their daily diet.
In this case, these supplements are:
- Magnesium: By default, low levels of magnesium in the body tend to produce contractions in the muscles and/or abdominal area, as this electrolyte is responsible for regulating the functioning of the muscular system. Therefore, to soothe the condition, it is appropriate to ingest magnesium through the following natural foods: spinach, avocado, nuts, lentils, chickpeas and dark chocolate.
- Potassium: This is a mineral that prevents the onset of cramps, because it improves the functioning of the muscles and the nervous system, as well as promoting water balance and optimising a constant heart rate. In this sense, it is good to eat foods that provide a good dose of potassium naturally, among which are: banana, papaya, kiwi, broccoli, spinach, tomato, milk, yoghurt, fish and red meat.
- Vitamin B1: Thiamine or vitamin B1 is defined as a dietary supplement used to attenuate the discomfort generated by contractions in the body. In addition, this vitamin is important for the growth, development and functioning of the body's cells, as well as for improving the functioning of the brain and acquiring much more energy. If you want to consume vitamin B1 naturally, it is essential that you eat: ginger, eggs, tuna, peas, rice, nuts, pulses, seeds, bread and cereals.
Medicines
In case the abdominal pain caused by stomach spasm is severe and accompanied by fever, blood in the stool, weight loss and these symptoms are prolonged for a long time, it is advisable to consult a professional doctor in the area.
He or she will be able to study your case in detail and provide a clear diagnosis. In this way, he or she will be able to prescribe a treatment that will be effective in alleviating the discomfort in question, taking into consideration some fundamental parameters such as: your medical history, your age, your state of health, your tolerance to drugs and the severity of the condition.
Consequently, it is not advisable to self-medicate and/or take any drug without first consulting a doctor, as this could trigger dangerous side effects in your body (nausea, diarrhoea, dizziness, fainting, drowsiness, dependence, addiction and even cardiac arrest, for example).
What are the most effective prevention methods for abdominal cramps due to gas colic?
Now, just as it is possible to soothe the pain of gas cramps, there are several prevention methods that can help you avoid suffering from the symptoms or signs of gas cramps. By means of these formulas, your body will have the necessary tools to make it more difficult for sudden spasms to appear in the abdominal area.
The following are the most solid methods to do so:
- Maintain a good level of hydration: It is paramount that you drink plenty of water or other clear liquids throughout the day, so that you can avoid dehydration leading to gas accumulation in the stomach and causing contractures. In this case, it is recommended to avoid sodas and coffee.
- Minimise the effects of stress on digestion: It is also ideal to avoid stress and/or anxiety so that the body does not become stressed and, as a consequence, tends to cramp during digestion. For this, you can use the relaxation techniques you like best (yoga, meditation, aromatherapy, music therapy, etc.).
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet: Eating foods rich in vitamins and minerals will allow the stomach to perform its functions correctly and it will not be altered by the low levels of potassium, magnesium and vitamin B1 that cause the ailment. It is also important to avoid eating fried foods, citrus fruits, spicy foods and alcohol.
- Exercise every day: If you incorporate daily training, all your muscles will be able to keep in good condition and it will be more difficult for them to contract, so they will not spasm. Apart from that, physical exercise manages to combat stress, which is one of the main causes of cramps in the abdominal area. It should be noted that it is essential to do it gradually.
- Eat smaller meals and be sure to chew well: This improves the digestion process because it triggers the production of stomach acid and pancreatic juices along the digestive tract. Additionally, it increases the absorption of nutrients, avoids gas agglomeration and even reduces stress. Keep in mind that it is recommended to mash food 25 to 50 times.
References
- Yang, N. Y., & Kim, S. D. (2016). Effects of a yoga program on menstrual cramps and menstrual distress in undergraduate students with primary dysmenorrhea: a single-blind, randomized controlled trial. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 22(9), 732-738. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/acm.2016.0058
- Eby, G. A. (2007). Zinc treatment prevents dysmenorrhea. Medical Hypotheses, 69(2), 297-301. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306987706009066
- Kim, J. S., Jo, Y. J., & Hwang, S. K. (2005). The effects of abdominal meridian massage on menstrual cramps and dysmenorrhea in full-time employed women. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing, 35(7), 1325-1332. https://synapse.koreamed.org/articles/1063323
- Lauretti, G. R., Oliveira, R., Parada, F., & Mattos, A. L. (2015). The new portable transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device was efficacious in the control of primary dysmenorrhea cramp pain. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface, 18(6), 522-527. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1094715921017311
- Han, S. H., Ro, Y. J., & Hur, M. H. (2001). Effects of aromatherapy on menstrual cramps and dysmenorrhea in college student woman: A blind randomized clinical trial. Korean Journal of Adult Nursing, 13(3), 420-430. https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO200125458753961.page
- Deligeoroglou, E. (2000). Dysmenorrhea. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 900(1), 237-244. https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06235.x
- Harel, Z. (2008). Dysmenorrhea in adolescents. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1135(1), 185-195. https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1196/annals.1429.007
- Iacovides, S., Avidon, I., & Baker, F. C. (2015). What we know about primary dysmenorrhea today: a critical review. Human reproduction update, 21(6), 762-778. https://academic.oup.com/humupd/article/21/6/762/628858
- Granot, M., Yarnitsky, D., Itskovitz-Eldor, J., Granovsky, Y., Peer, E., & Zimmer, E. Z. (2001). Pain perception in women with dysmenorrhea. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 98(3), 407-411. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S002978440101465X
- Grandi, G., Ferrari, S., Xholli, A., Cannoletta, M., Palma, F., Romani, C., ... & Cagnacci, A. (2012). Prevalence of menstrual pain in young women: what is dysmenorrhea?. Journal of pain research, 169-174. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.2147/JPR.S30602