- What are cervical muscle strains in the neck and trapezius?
- What are the causes of muscular strains in the neck?
- Best products for neck strains
- Main signs and symptoms associated with cervical muscle strains
- How to relieve pain and improve symptoms from neck and trapezius muscle strains?
- What are the most effective prevention methods for neck and trapezius muscle pulls?
Cervical muscle strains that occur in the neck and trapezius are capable of generating pain and muscular immobility. For this reason, it is necessary for you to know what a muscle pull in this area of the body is and why it originates. This information is explained in a simple way in the following paragraphs.
In addition, you will be able to read about the symptoms associated with cervical spine strains and how you can alleviate the pain by means of the different treatments and complementary therapies currently available. Don't miss out.
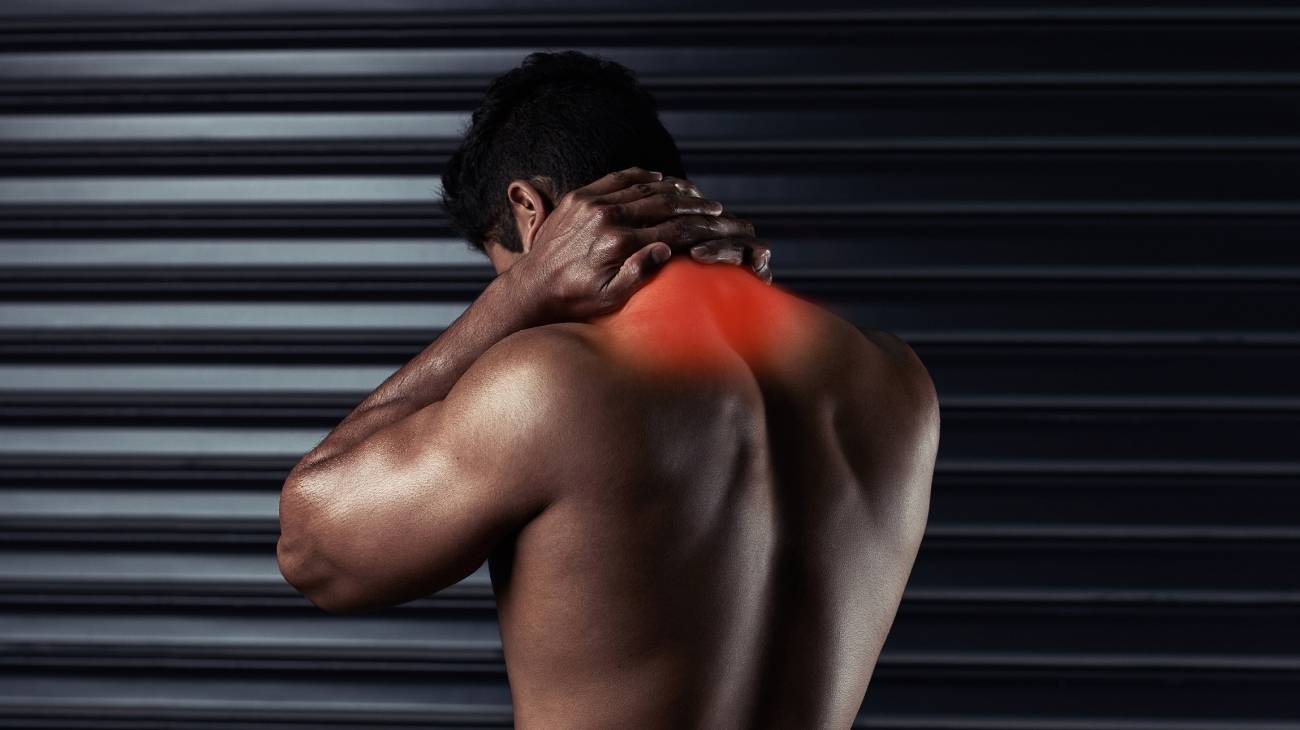
What are cervical muscle strains in the neck and trapezius?
Muscle strains in the cervical area are caused by the inability of the blood to exchange nutrients and gases with the soft tissue fibres in this part of the body. This causes toxic waste, which is generated during activity, to become lodged in the muscles of the neck, thus causing unconscious tension on the part of the person.
This muscle stiffness causes pain, loss of sensation and inflammation in the cervical neck. There are different causes of this type of illness and treatments that can be applied, but we will analyse these in the following paragraphs.
What are the causes of muscular strains in the neck?
There are different factors that cause the presence of distensions in the trapezius and neck. Find out what these causes are
- Excessive muscle strain: Overexertion can lead to strains in the trapezius and neck muscles, causing involuntary tension in this part of the body.
- Lack of rest: It is feasible that physical activity forces the muscle structure to rest, but if the tissues have not been at rest long enough, the amount of metabolites in the fibres will cause a muscle pull.
- Age: Although this type of inflammatory disease can appear in any type of patient, it is common to find athletes, workers and, above all, people over 60 years of age with this type of ailment. In the latter case, the injury is caused by the loss of elasticity of the musculature.
- Lack of magnesium and other micronutrients: Magnesium, like potassium and sodium, are essential nutrients for the proper functioning of the muscles. When there is an inadequate amount of these elements, the fibres of the tissues do not have sufficient elasticity, leading to the appearance of neck strains.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of activity in the muscles can lead to the appearance of muscle strains. Therefore, every time you want to move or exert force with the trapezius or sternocleidomastoid muscles, this activity can cause the muscles to pull.
- Lack of stretching and mobility: Stretching is essential to keep all muscles under normal tension. Lack of frequent stretching increases the likelihood of muscle strain.
- Lack of warm-up: Before doing any kind of activity, it is necessary to warm up the muscular structure so that strains are not used. For this reason, anyone who plays a sport or has to exert force on this part of the body should start moving the muscles gradually.
- Stress: Worries and any kind of frustrating thoughts expose the person to unconscious muscle contraction. This increases the likelihood of muscle strain in the neck and trapezius.
- Cold temperatures: It should not be forgotten that muscles react with contraction to cold. Based on this, it is important to bear in mind that sleeping or staying in cold places without proper protection can lead to neck strains.
- Poor nutrition: these habits can lead to muscle twitching in this area of the body. This must also be taken into account with a lack of hydration.
Best products for neck strains
Bestseller
-
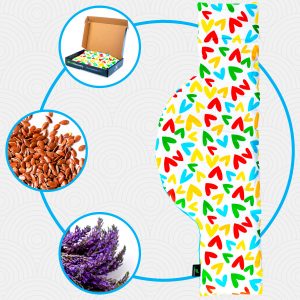
Acupressure Mat and Pillow (Black/Gray)
$49.95 -
Acupressure Mat and Pillow (Green/Navy)
$49.95 -
Acupressure Mat and Pillow (Pink/Bordeaux)
$49.95 -
Acupressure Pillow (Black/Gray)
$29.46 -
Acupressure Pillow (Green/Navy)
$29.46 -
Acupressure Pillow (Pink/Bordeaux)
$29.46 -
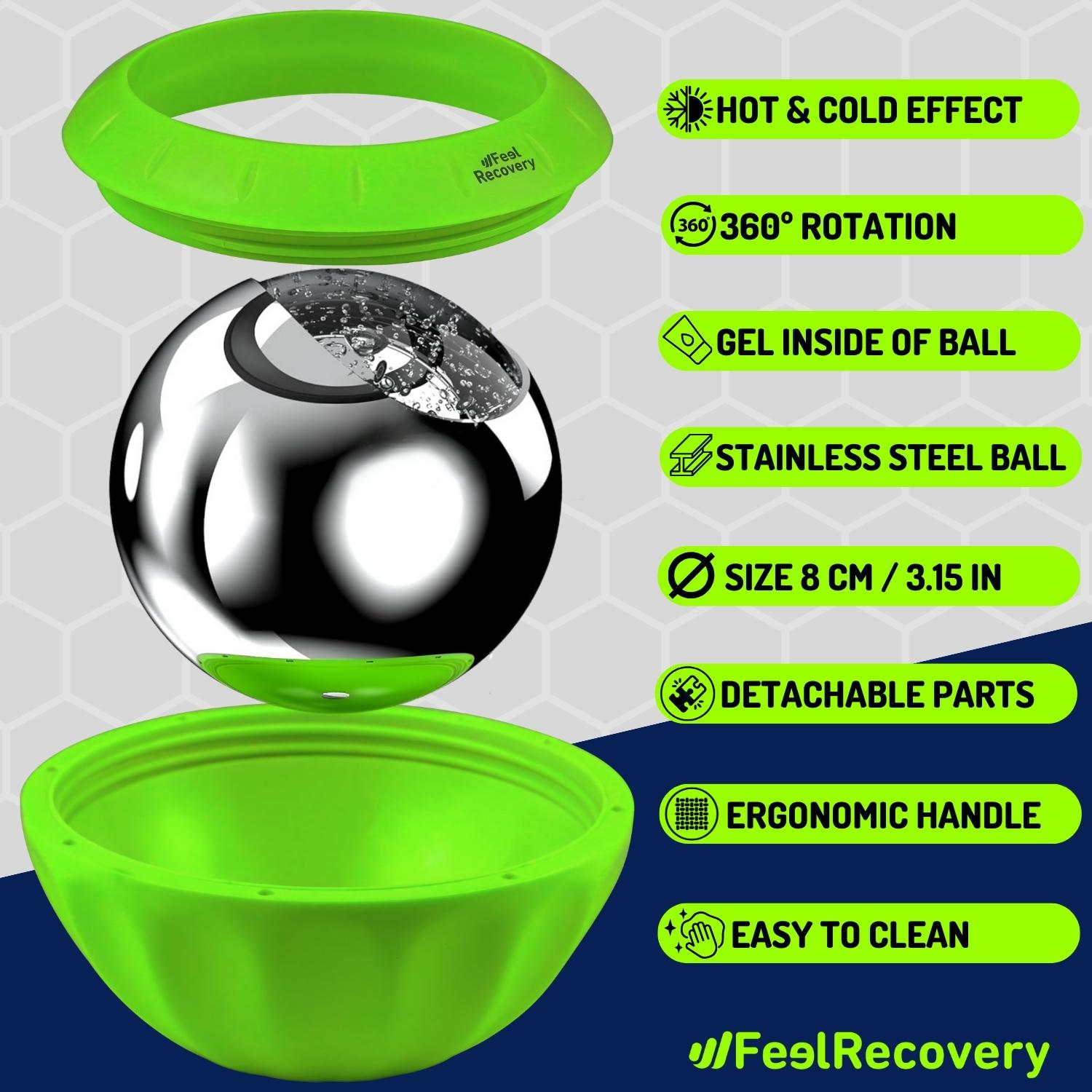
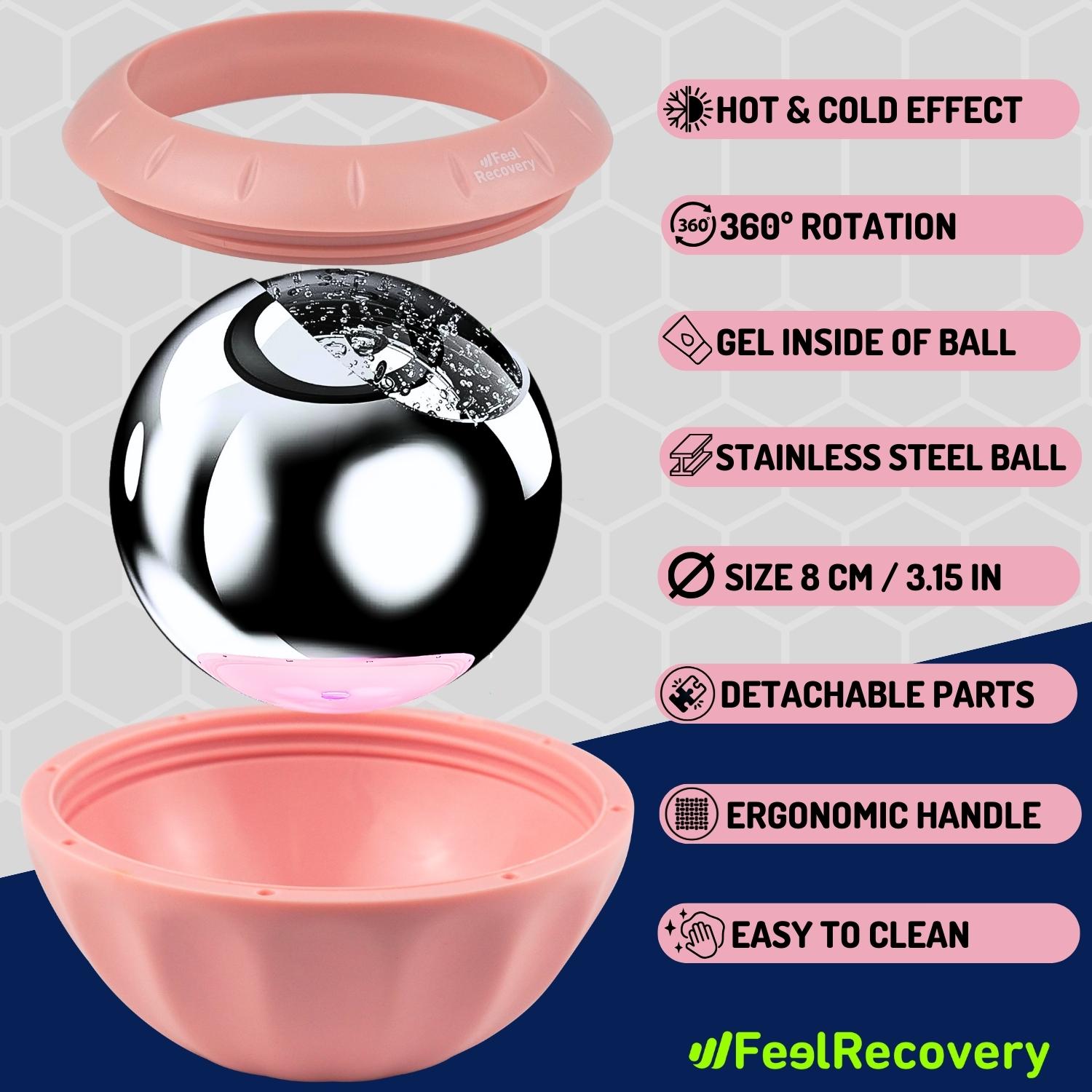
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Black)
$39.95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Green)
$39.95 -
Ice Massage Roller Ball (Pink)
$39.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Hearts)
$24.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Oxford)
$24.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck & Shoulder Pain Relief (Sport)
$24.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck Pain Relief (Hearts)
$19.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck Pain Relief (Oxford)
$19.95 -
Microwave Heating Pad for Neck Pain Relief (Sport)
$19.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Hearts)
$19.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Oxford)
$19.95 -
Microwaveable Heating Pad for Pain Relief (Sport)
$19.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Black)
$24.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Green)
$24.95 -
Shoulder Support Brace (Pink)
$24.95 -
Trigger Point Massage Stick (Black)
$14.95 -
Trigger Point Massage Stick (Green)
$14.95 -
Trigger Point Massage Stick (Pink)
$14.95
Main signs and symptoms associated with cervical muscle strains
You should be aware of the following symptoms that may appear in your body because they could be associated with trapezius, sternocleidomastoid and neck strains
- Headache at the base of the skull: Cervical contracture can cause localised headache in the upper part of the neck.
- Pain in the soft tissues located in the area: It is feasible to feel stiffness and pain in the trapezius, sternocleidomastoid and splenius muscles.
- Muscle stiffness: Muscle strains in this area of the body can cause the muscle structure to remain tight due to the large amount of metabolites found in the fibres.
- Tinnitus: Ringing in the ears may occur in some patients withtinnitus. It can also cause disturbances in night-time sleep and memory.
- Difficulty moving the neck: Somewhat related to the previous point, as the stiffness in the muscles will cause the patient to feel pain when wishing to move the neck and shoulder.
- Paresthesia: Tingling sensation and loss of sensation is common in more advanced cases of this type of injury. This symptom can appear in the neck as well as in the shoulder and arms.
- Swelling: In some cases swelling becomes visible in this muscle area. This is due to the accumulation of blood that cannot circulate properly.
- Appearance of lumps: The manifestation of nodules is another common symptom of neck muscle pulls. These are caused by the patient's involuntary tension of the sternocleidomastoid or splenius.
- Dizziness: Fatigue and stress can cause dizziness if there is muscle strain in the neck.
How to relieve pain and improve symptoms from neck and trapezius muscle strains?
To improve the symptoms of inflammation and muscle stiffness in the tissues located in the neck and trapezius it is possible to implement some of the treatments we will show you below.
Alternative and complementary therapies
These types of treatments are used to improve the symptoms in the cervical region of the neck. See below which are the most commonly applied at present:
- Heat and cold therapy: It is possible to apply heat and cold therapy, but it should be noted that cold alone is not suitable for neck and trapezius strains. For this reason, the implementation of this therapy should be directed by a professional so that the temperature is not freezing, as this will cause the muscles to contract more. The session should not exceed 20 minutes starting and ending with the heat. Different elements are used to obtain the benefits of both temperatures, the most common being water bags, electric blankets and special gels. It should not be forgotten that cold helps to deflate the area while heat allows better blood circulation.
- Compression therapy: This type of therapy consists of applying special collars or bandages to the trapezius so that the muscles remain pressed with the correct tension. This will not only help the muscles to rest, but will also stimulate the blood vessels so that the blood flows better in this area and eliminates all the metabolites that remain in the neck.
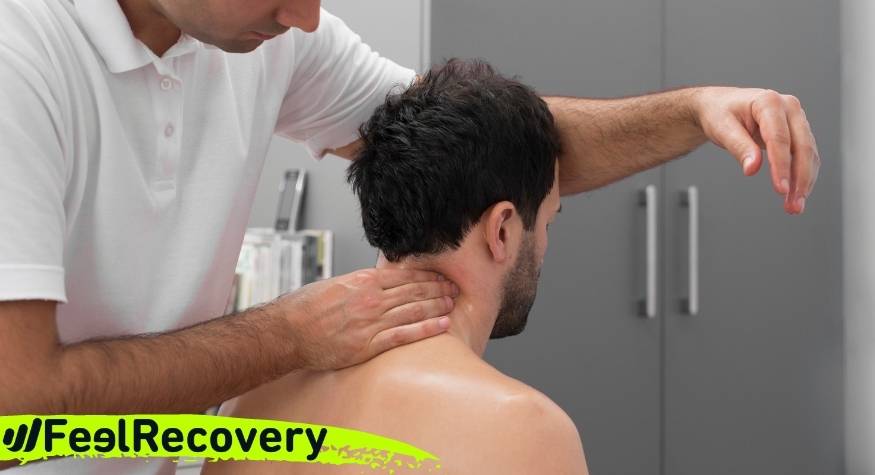
- Massage therapy: Massage is one of the most commonly used complementary treatments for this type of injury. The aim is to rub the muscles, through different techniques, to get the neck and trapezius to eliminate residual molecules found in the tissue. This will help to receive more blood flow, achieving the exchange of nutrients and oxygen with the muscle. This increases the patient's sense of well-being, improves movement and decreases inflammation in the area.
- Acupressure therapy: The aim of this therapy is to achieve mental harmony in the patient so that stress is reduced and the muscular tension in the trapezius and neck is reduced. In other words, thanks to the pressure generated by the professional's fingers and palms, the central nervous system is stimulated to achieve general wellbeing.
- Thermotherapy: Although we have already mentioned some of the benefits of high temperatures in cold and heat therapy, it is necessary to go into the advantages of thermotherapy, as this technique only uses heat on the neck and trapezius. By means of warm compresses, electrotherapy, water bags or blankets it is possible to stimulate the arterioles and venules so that the walls of the capillaries are better connected and more blood is supplied to the affected area. In this way it is possible to make the exchange of gases and liquids between the blood and the muscles more efficient.
- Natural remedies using plants: There are different plants that have anti-inflammatory and relaxing properties that can be applied in the treatment of a muscle strain injury in the trapezius and neck. In other words, they are used by means of natural herbal concoctions so that they have a similar effect to drugs applied in a conventional therapy. It should be borne in mind that these plants must be recommended for use by a doctor. The most common medicinal plants include lavender, boldo, laurel and thyme.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: In order to avoid future injuries to the trapezius and neck, it is necessary to assimilate different actions and lifestyle habits that improve the patient's health. Within this set of recommendations that the doctor will make are the correct postures that the person should implement in each daily action that he/she performs. In addition, it will be necessary to incorporate vegetables, fruit and foods rich in sodium, potassium and magnesium into the diet; the necessary rest time and the importance of avoiding excessive strain on the muscles.
Nutritional supplements
This type of complementary nutrients helps the patient to include in his diet chemical components necessary for the proper functioning of the muscular structure, especially that of the neck and trapezius. For this reason, only a doctor can prescribe the incorporation of B vitamins, vitamin D, vitamin E, omega 3, magnesium, calcium and potassium. These supplements are available in different forms, the most common being powder and capsules.
Physiotherapy treatments
Physical therapies aim to stimulate the muscular structure located in the trapezius, sternocleidomastoid and neck. They can be done by different techniques, the most used by physiotherapists being electrotherapy, ultrasound and laser application. In this way the capillary walls are stimulated by means of heat, which can be superficial or internal. The most commonly used physical exercises are those that are repetitive and of short duration, and in some cases they can be practised under water.
Medications
Pharmacological therapy must be administered and supervised by a doctor, so self-medication is never recommended. This is because anti-inflammatory and opioid analgesics can cause adverse situations if they are not applied with the correct doses and frequency.
It is also possible to find in this treatment patients who must use muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For example, Paracetamol, Diazepam and Hydrocodone are some of the drugs prescribed to combat this type of injury.
What are the most effective prevention methods for neck and trapezius muscle pulls?
See below for the most effective prevention methods to avoid neck and trapezius muscle pulls
- Avoid the cold or staying in places with low temperatures: This will help you to avoid involuntary contraction of the cervical muscles, which can lead to the onset of a pulled muscle.
- Rest the entire soft tissue structure: It is necessary for the neck and trapezius muscles to rest between activities, especially when playing sports or working with repetitive movements.
- Try not to do demanding activities: Don't forget that excessive strain on the neck and trapezius muscles can cause involuntary muscle tension in this area. Therefore, if for some reason you must carry out these tasks, do not forget to use adequate protection.
- Practice meditation: Relaxation and massage therapies help to reduce stress and worries in people suffering from a neck muscle strain. It also helps to find a sustainable emotional balance to cope with the problems and pains of illness.
- Always choose a nutrient-rich and balanced diet: Good nutrition and proper hydration will help keep your muscles in good condition. For this reason, the incorporation of magnesium and calcium will accompany you in this objective.
- Warm up your muscle structure before starting an activity: This will prevent your muscles from overexerting themselves and starting the task abruptly, which can lead to neck strains. Don't forget that it is also important to stretch this area properly.
- Try walking and aerobic exercise: Cycling or walking will help you to avoid a sedentary lifestyle, which will benefit the functioning of the tissue fibres.
- Maintain correct posture throughout the day: This will help to correct the alignment between the neck and head so that the muscles do not exert undue strain.
References
- Vasavada, A. N., Brault, J. R., & Siegmund, G. P. (2007). Musculotendon and fascicle strains in anterior and posterior neck muscles during whiplash injury. Spine, 32(7), 756-765. https://journals.lww.com/spinejournal/Abstract/2007/04010/Musculotendon_and_Fascicle_Strains_in_Anterior_and.9.aspx
- Sovelius, R., Oksa, J., Rintala, H., Huhtala, H., & Siitonen, S. (2008). Neck muscle strain when wearing helmet and NVG during acceleration on a trampoline. Aviation, space, and environmental medicine, 79(2), 112-116. https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/asma/asem/2008/00000079/00000002/art00006
- Alvarez, V. S., Halldin, P., & Kleiven, S. (2014). The influence of neck muscle tonus and posture on brain tissue strain in pedestrian head impacts (No. 2014-22-0003). SAE Technical Paper. https://www.sae.org/publications/technical-papers/content/2014-22-0003/
- Benyamin, R., Singh, V., Parr, A. T., Conn, A., Diwan, S., & Abdi, S. (2009). Systematic review of the effectiveness of cervical epidurals in the management of chronic neck pain. Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE): Quality-assessed Reviews [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK78352/
- Powell, F. C., Hanigan, W. C., & Olivero, W. C. (1993). A risk/benefit analysis of spinal manipulation therapy for relief of lumbar or cervical pain. Neurosurgery, 33(1), 73-79. https://journals.lww.com/neurosurgery/Abstract/1993/07000/A_Risk_Benefit_Analysis_of_Spinal_Manipulation.11.aspx
- Glick, J. M. (1980). Muscle strains: prevention and treatment. The Physician and sportsmedicine, 8(11), 73-77. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00913847.1980.11710969
- Garrett Jr, W. E. (1996). Muscle strain injuries. The American journal of sports medicine, 24(6_suppl), S2-S8. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/036354659602406S02
- Orchard, J., Best, T. M., & Verrall, G. M. (2005). Return to play following muscle strains. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, 15(6), 436-441. https://journals.lww.com/cjsportsmed/Abstract/2005/11000/Return_to_Play_Following_Muscle_Strains.8.aspx
- Garrett Jr, W. E. (1990). Muscle strain injuries: clinical and basic aspects. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 22(4), 436-443. https://europepmc.org/article/med/2205779
- Järvinen, T. A., Kääriäinen, M., Järvinen, M., & Kalimo, H. (2000). Muscle strain injuries. Current opinion in rheumatology, 12(2), 155-161. https://journals.lww.com/co-rheumatology/Abstract/2000/03000/Muscle_strain_injuries.10.aspx